Cao Bang Province:
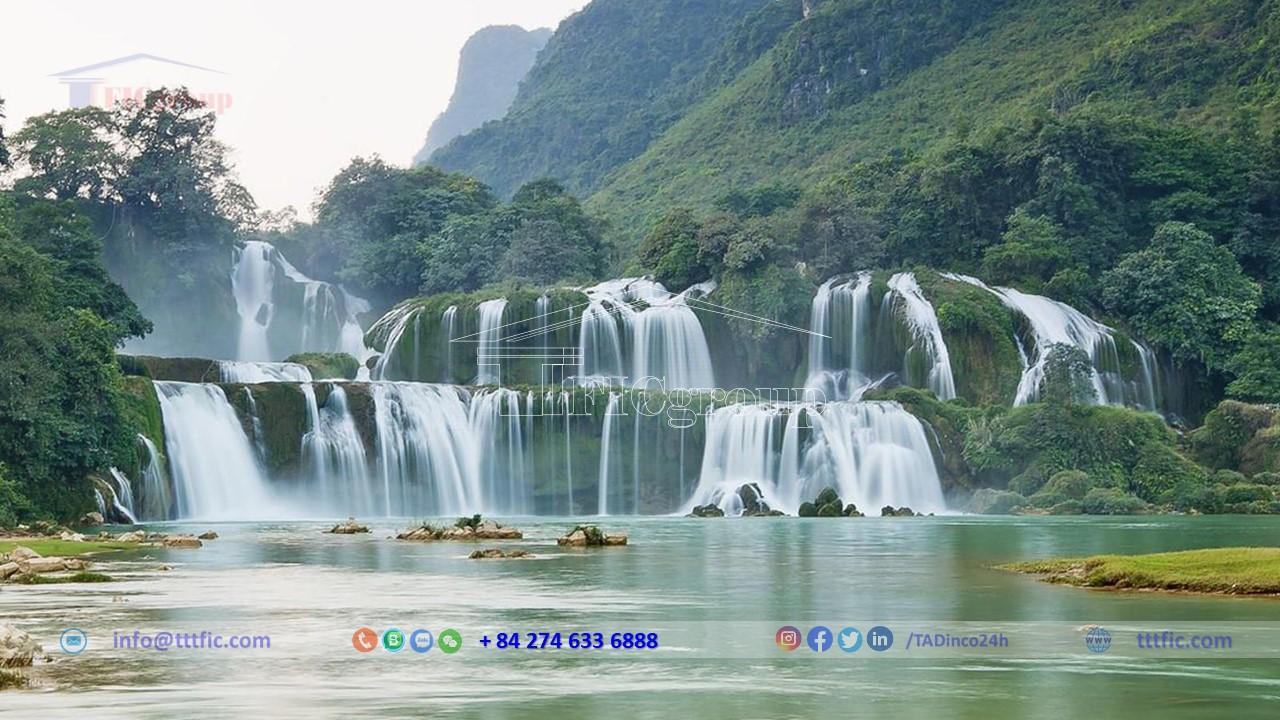
Cao Bang province, located in Northeast Vietnam, is a border province in the northeast of the country, adjacent to China. It boasts a mountainous terrain, including famous mountain ranges like Hoa An, Bao Lam, and Cao Bằng. The Ban Gioc Waterfall, situated on the Vietnam-China border, is a renowned tourist destination in the province.
Abundant in natural resources, Cao Bằng is known for its waterfalls, rivers, and alluvial plains. The province also boasts historical relics and scenic spots. Notable among them are the Temple of the Fatherland, marking the beginning of the resistance against the French, and the former capital of the Tây Trạch kingdom, Tây Trạch Ancient Citadel.
The majority of Cao Bằng’s population comprises ethnic minorities, including the Dao, Tày, Nùng, and H’Mông people. It is a culturally diverse region with a rich traditional heritage, featuring traditional music, puppetry, and vibrant festivals.
Geography:
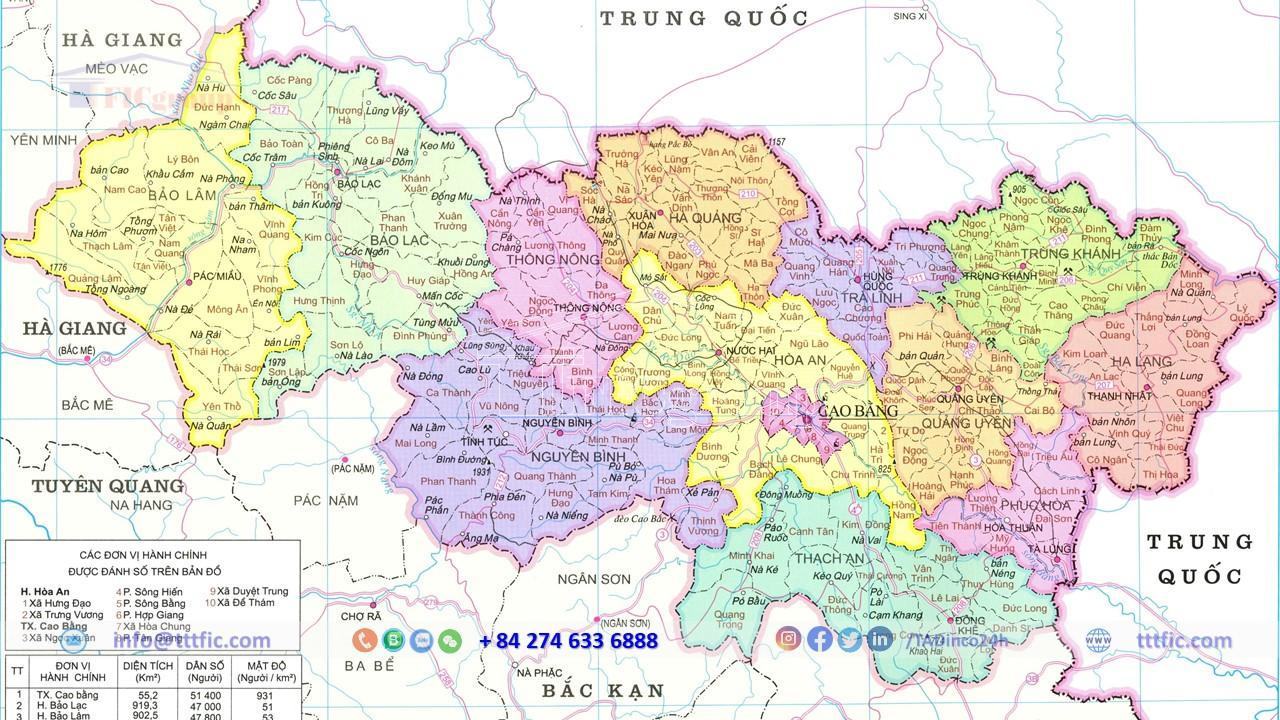
Cao Bằng province is located in the northeast of Vietnam, with the following geographical positions:
- It shares a border of 333,125 km with the Choang Quảng Tây Autonomous Region (China) in the north and northeast.
- It is bordered by Hà Giang province to the west.
- It is adjacent to Tuyên Quang province in the southwest.
- It shares borders with Bắc Kạn and Lạng Sơn provinces in the south.
The extreme points of Cao Bằng province are as follows:
- Northernmost point: Lũng Mẩn hamlet, Đức Hạnh commune, Bảo Lâm district.
- Easternmost point: Lý Quốc commune, Hạ Lang district.
- Westernmost point: Quảng Lâm commune, Bảo Lâm district.
- Southernmost point: Na Phai hamlet, Trọng Con commune, Thạch An district.
The administrative center of the province is Cao Bằng City, located 279 km from Hanoi. The province stretches approximately 80 km from north to south, ranging from 23°7’12″N to 22°21’21″N (from Trọng Con commune, Thạch An district to Đức Hạnh commune, Bảo Lâm district). It has a width of about 170 km from east to west, ranging from 105°16’15″E to 106°50’25″E (from Quảng Lâm commune, Bảo Lâm district to Lý Quốc commune, Hạ Lang district). The geographic center of the province is located in Trương Lương commune, Hòa An district.
Natural condition:
Cao Bằng province spans 6,690.72 km² of natural land, consisting of a limestone plateau mixed with mountains that reach an average height of over 200 meters, with the border area ranging from 600 to 1,300 meters above sea level. The province is characterized by overlapping mountains, where mountainous forests cover more than 90% of the land, creating three distinct regions: rocky mountains in the east, a combination of mountains and land in the west, and predominantly mountainous land with dense forests in the southwest.
The province is intersected by major rivers, including the Gâm River in the west and the Bằng Giang River in the central and eastern regions, as well as other rivers like Quây Sơn, Bắc Vọng, Nho Quế, Năng, Neo, and Hiến.
Forests blanket the majority of Cao Bằng’s land, ensuring relatively clean air in rural, residential, and urban areas. The main roads experience low levels of dust pollution due to fewer vehicles and a sparse population. However, improper waste disposal by some individuals and sand mining activities have polluted the river water sources, impacting the local ecosystem. Motorcycles dominate transportation in the province, resulting in low fuel consumption and reduced greenhouse gas emissions and other harmful pollutants. As a result, Cao Bằng stands out as one of the provinces in Vietnam with a cleaner and less polluted climate compared to other regions.
Climate:
Cao Bằng province enjoys a pleasant climate, with a humid subtropical climate influenced by cold air masses from the north. The terrain facilitates wind circulation. Temperatures never fall below 0°C, and snow is rare, except in high mountainous areas.
Summers are hot and humid, with average highs of 30-32°C and lows of 23-25°C. Extreme temperatures of 39-40°C are uncommon. In winter, Cao Bằng experiences a temperate climate due to its wind-receiving terrain. Lows range from 5-8°C, highs from 15-28°C, with the coldest months being December, January, and February, when temperatures can drop to 6-8°C. The season begins with dry air and low humidity.
Spring and autumn have less distinct characteristics, with unpredictable weather. Spring is often muggy, while autumn is cool and pleasant.

Economy of Cao Bang Province:
According to the announcement by the General Statistics Office, the estimated growth rate of Gross Regional Domestic Product (GRDP) in Cao Bằng province in 2022 increased by 5.04% compared to the same period last year. This growth rate is higher than the 3.34% increase in 2021, thanks to the effective control of the pandemic, widespread vaccination campaigns, and the reopening of the economy. The industrial and service sectors are experiencing a strong recovery.
In terms of overall economic growth, the agricultural, forestry, and fisheries sector increased by 3%, contributing 0.65 percentage points to the total value added growth rate. The industrial and construction sector grew by 3.91%, contributing 0.84 percentage points (with the industrial sector growing by 11.46%, contributing 0.88 percentage points). The service sector is the main driving force behind economic growth, with a growth rate of 6.01%, contributing 3.2 percentage points. This impressive growth indicates a strong recovery in the market-oriented service sectors, following the negative impacts of the Covid-19 pandemic in the previous two years (service sector growth was 5.26% in 2020 and 4.16% in 2021). Product taxes minus subsidies increased by 9.73%, contributing 0.35 percentage points to the total value added growth rate.
With a relatively high economic growth rate, the scale of the economy is expanding. Based on current prices, the estimated GRDP in 2022 reached 21,634.76 billion VND, and the per capita GRDP is estimated to be 39.84 million VND, an increase of 2.66 million VND compared to 2021. In terms of economic structure, the agricultural, forestry, and fisheries sector accounted for 21.74% with 4,703.18 billion VND, the industrial and construction sector accounted for 20.76% with 4,491.02 billion VND, the service sector accounted for 53.75% with 11,628.07 billion VND, and product taxes minus subsidies accounted for 3.75% with 812.49 billion VND.
Agriculture, forestry, aquaculture:
Agriculture
Crop:
In 2022, the agricultural sector in the province of Cao Bằng faced challenges but received strong support from local authorities and departments. Despite difficulties, the province’s agricultural production achieved satisfactory results. During the winter-spring season, the cultivated area increased slightly, particularly in rice, tobacco, and other perennial crops. However, grain production experienced a slight decrease compared to the previous season but still exceeded the plan. In the main season, the total cultivated area expanded, with rice cultivation showing significant growth in several districts. Grain production in this season also increased, surpassing the previous year’s output.
Additionally, the production of flowers and some perennial crops, such as cassava, soybeans, peanuts, and sugarcane, exhibited positive growth. Overall, the agricultural sector demonstrated resilience and benefited from proactive measures, including the promotion of agricultural activities, the encouragement of crop restructuring, mechanization, and the application of scientific achievements. These efforts led to improved productivity and contributed to the province’s overall agricultural development. Despite the challenges faced, the agricultural sector in Cao Bằng showed promising signs of progress, emphasizing the resilience and determination of local farmers and the effectiveness of supportive measures implemented by local authorities.

Breed:
In 2022, livestock production in Cao Bằng province remained relatively stable, with successful control of foot-and-mouth disease and African swine fever. The veterinary work received close attention and guidance from relevant departments, actively vaccinating and disinfecting animal farms. Strict management of slaughter and internal transportation helped control the spread of diseases, resulting in increased livestock numbers compared to 2021. The total number of buffaloes reached 106,756, up 0.64%, while the number of cattle reached 107,529, up 2.22%. However, the production of buffalo and cattle meat decreased due to the impact of COVID-19 and strict measures imposed by China on cross-border trade.
The total number of pigs increased by 6.28% to 325,291, and pig meat production rose by 2.97% to 26,132 tons. The control of African swine fever allowed farmers to expand their pig farming operations. Poultry numbers also saw an increase of 2.06% to 3,057.13 thousand, with poultry meat production reaching 6,759 tons and egg production totaling 39,315 thousand. Disease outbreaks such as foot-and-mouth disease and African swine fever occurred sporadically in some areas, resulting in the culling of affected animals. Despite these challenges, the livestock sector in Cao Bằng demonstrated resilience and received support from local authorities and departments in disease control and livestock development.
Forestry:
In 2022, favorable weather conditions facilitated forestry production and led to an increase in newly planted forests. The focus was on large timber production, enhancing the value of diverse forest types. Forest cover continued to grow. Measures were implemented to effectively address issues like illegal logging and timber transportation. Local monitoring and extensive communication efforts promoted forest management, protection, and fire prevention at the community level.
The estimated area of newly planted forests in 2022 decreased by 5.22% to 3,035 hectares. The main tree species planted included pine, cinnamon, cajeput, oak, sassafras, and acacia. Most of these forests were managed by households who purchased seedlings for reforestation or received contracted protection areas.
The cared-for forest area in 2022 increased by 8.72% to 8,387 hectares due to the expansion of newly planted forests and ongoing care for previously established ones.
Regenerating forests under protection expanded by 1.32% to 108,568 hectares, involving transfers of protected areas and the addition of natural forests with low coverage rates.
Forests under contracted protection significantly increased by 42.42% to 220,160 hectares. Enhanced forest management and protection ensured compliance with objectives.
The total volume of harvested timber in 2022 decreased by 9.10% to 24,945 cubic meters, while firewood production increased slightly to 763,101 steres.
Various forest products, such as bamboo, nuts, wild plum, and medicinal herbs, experienced growth in production.
Forest damage in 2022 amounted to 53.16 hectares, with fire and forest destruction being the primary causes. The province faced challenges in managing and preventing these incidents throughout the year.
Aquaculture:
Aquaculture production in December was stable, with a focus on caring for and harvesting from aquaculture areas. Fishing for aquatic products in rivers and streams continued, but the catch volume was low, primarily for household consumption.
In 2022, aquaculture and fishing activities in the province showed positive development. Favorable weather, stable prices, and market demand encouraged investment in caring for and cultivating economically valuable species. Aquaculture and fishing production increased, significantly contributing to the local food supply.
The total aquaculture production in 2022 reached 598.85 tons, with fish accounting for 582 tons, shrimp 2.48 tons, and other aquatic products 14.37 tons. Aquaculture production increased by 0.74% compared to the previous year.
Fish farming accounted for the majority of aquaculture, with carp, tilapia, catfish, and trout being the main species. Efforts were made to improve efficiency by selecting high-quality breeds, managing feed sources, and ensuring proper pond sanitation.
The total fishing production in 2022 reached 115.35 tons, including 100.47 tons of fish, 2.48 tons of shrimp, and 12.4 tons of other aquatic products. Fishing activities were driven by consumer preference for natural seafood, contributing to household income and livelihood improvement.
Overall, aquaculture and fishing activities experienced positive growth, supported by favorable conditions and market demand, ensuring a stable food supply for the province.

Industry:
Industrial production in 2022 showed a positive and dynamic trend, with growth in the first three quarters and a slowdown in the fourth quarter. The industrial production index increased by 10.29% compared to 2021. The mining sector, electricity production and distribution, and water supply, waste management, and treatment activities experienced growth, while the processing and manufacturing sector declined.
In December 2022, the industrial production index increased by 10.23% compared to the previous month and by 12.59% compared to the same period last year. Mining, electricity production and distribution, and water supply, waste management, and treatment activities saw significant increases, while the processing and manufacturing sector decreased.
For the entire year of 2022, the industrial production index increased by 10.29%. The mining sector and electricity production and distribution were the driving forces behind the growth, while the processing and manufacturing sector declined.
Certain products experienced growth, such as purified water, electricity production, bricks, cement, and manganese ore. However, products like building stone, manganese, natural sand, and non-alloy iron and steel saw decreases.
The consumption index in the processing and manufacturing sector decreased in December 2022 compared to the same period last year but increased compared to the previous month. Overall, the consumption index for the entire year decreased, with significant declines in the production of cast metal products and wood processing.
Inventory levels in the processing and manufacturing sector decreased in December 2022, with notable decreases in food processing and printing services. However, the production of other non-metallic mineral products and wood processing saw increased inventory levels.
The labor utilization index in industrial enterprises decreased in December 2022 compared to the previous month and the same period last year, with declines in both state-owned and foreign-invested enterprises.
Social:
The total population of Cao Bang province is 530,341 people, according to the population census on April 1, 2019, conducted by the Provincial Statistics Office [11]. The urban population is 123,407 people, while the rural population is 406,934 people. The urbanization rate in 2022 is 23.2%.
The ethnic groups in Cao Bang include the Tay, with a population of 216,577 (accounting for 40.84% of the total population), the Nung with 158,114 people (29.81%), the Mong with 61,579 people (11.65%), the Dao with 54,947 people (10.36%), the Kinh with 27,170 people (5.12%), the San Chay with 7,908 people (1.49%), the Lo Lo with 2,861 people (0.54%), and other ethnic groups with 1,005 people (0.19%).