Dien Bien Province:
Dien Bien Province located on the western edge of the Northwest region, Dien Bien is 504 km west of the capital Hanoi. It is the only province that shares a border with two countries, Laos and China, spanning over 400 km. It is a province rich in tourism potential, particularly in the field of culture and history. Its most prominent feature is the system of historical relics associated with the Dien Bien Phu campaign. Additionally, Dien Bien is home to the landmarks A Pa Chai and the Westernmost Point of the Fatherland.
The name Dien Bien was given by Emperor Thieu Tri in 1841, derived from Chau Ninh Bien. “Dien” means steadfast, and “Bien” means border or frontier. Hence, “Dien Bien” refers to the steadfast border region of the nation.
Area: 541 km²
Population: 613 500 people (2020)
Region: Northwest
Administrative divisions: 1 town, 1 city and 8 districts
Telephone code: 215
License plate: 27
Geography:
Dien Bien province is situated on the western edge of the Northwest region in Vietnam. It has geographical coordinates ranging from 20°54′ to 22°33′ north latitude and from 102°10′ to 103°36′ east longitude. Dien Bien province, situated at a distance of 504 km to the west of the capital Hanoi, shares borders with different regions. To the east and northeast lies Son La province, while the northern border is shared with Lai Chau province. Moving northwest, the province is adjacent to Yunnan province in China. On the western and southwestern side, Dien Bien shares its borders with Phongsali and Luang Prabang provinces of Laos.
Dien Bien is the only province that shares a border with two countries, Laos and China, spanning over 400 km. It has a border length of 360 km with Laos and 40.86 km with China.
The extreme points of the province are as follows:
- The northernmost point is in Sen Thuong commune, Muong Nhe district.
- The westernmost point is in A Pa Chai village, Sin Thau commune, Muong Nhe district.
- The easternmost point is in Ta Ma commune, Tuan Giao district.
- The southernmost point is in Muong Loi commune, Dien Bien district.
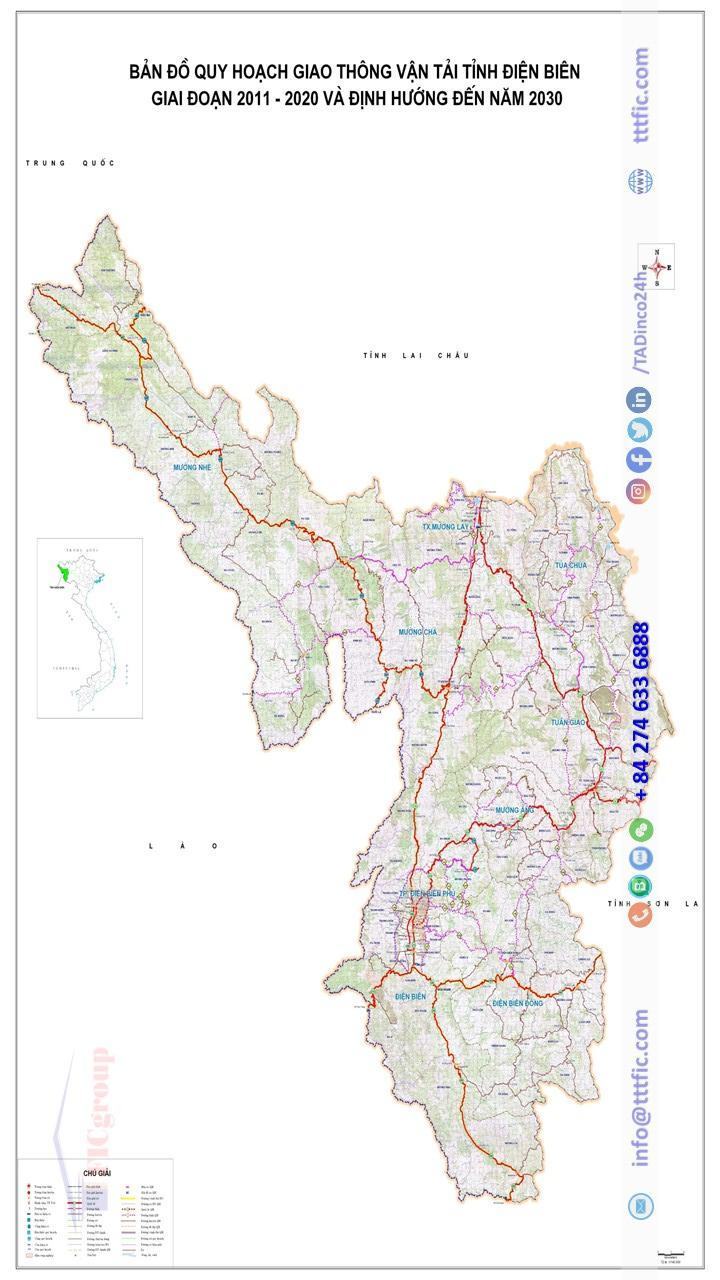
Topographic:
Dien Bien boasts a complex terrain characterized by steep hills and rugged mountains, creating challenging and fragmented landscapes. The province is formed by mountain ranges that run in a northwest-southeast direction, with varying elevations ranging from 200 m to over 1,800 m. The terrain gradually descends from north to south and slopes gently from west to east.
In the northern part, there are notable peaks such as 1,085 m, 1,162 m, and 1,856 m (located in Muong Nhe district), with the highest point being Pu Den Dinh peak at 1,886 m. Towards the west, there are peaks at 1,127 m, 1,649 m, 1,860 m, and a range of high points extending down to Tuan Giao. Interwoven with these high mountain ranges are valleys, narrow rivers, small streams, and distributed slopes throughout the province. Among them, the Muong Thanh valley forms the expansive Muong Thanh plain, spanning over 150 km². It is the largest and most renowned plain in Dien Bien province and the entire Northwest region.
Geological features:
Dien Bien has a long history of geological development and a complex tectonic structure. After a relatively stable period of geological formation during the Pliocene and Quaternary epochs, mountainous terrain was established, separating the land. The uplifting process led to the excavation and erosion of river valleys, resulting in increasingly deep valleys with slopes ranging from 300-400 m and steep cliffs with numerous waterfalls.
Land:
In Dien Bien, the land predominantly falls under the category of red-yellow soil (629,806.26 hectares) and black soil, with an additional significant area of alluvial soil (12,622.13 hectares) situated in the Mường Thanh valley.
Geological faults:
Dien Bien is the intersection of several deep fault zones: the Da River fault, the Ma River fault, the Dien Bien – Lai Chau fault, and the Son La fault. Among them, the Lai Chau – Dien Bien fault is actively stretching, causing significant subsidence and uplift on the eastern and western sides, resulting in intense fragmentation of the Earth’s crust. These factors have created typical landslide and debris flow areas, leading to phenomena such as floods and earthquakes. These faults play a crucial role in the formation and distribution of mineral resources in Dien Bien.
Mineral resources:
Dien Bien possesses diverse mineral resources, including mineral water, bituminous coal, limestone, black stone, granite, iron, lead, zinc, aluminum, copper, mercury, and more. Among these, coal, construction materials (such as cement), and mineral water can be extracted on a large scale, while the remaining resources are relatively low in quantity and scattered throughout the province. Currently, there are approximately 83 mines, mineral deposit sites, and mineral manifestations in Dien Bien. Bituminous coal is typically distributed in the districts of Dien Bien and Dien Bien Dong, while construction materials such as lead and zinc are found in Tuần Giáo and Tua Chua districts. Iron, copper, and antimony are located in Muong Cha district, and gold is found in Dien Bien Dong district. Limestone resources are abundant in Dien Bien district.
Climate:
Dien Bien experiences a highland tropical climate with distinct seasons. The winter is relatively cold with less rainfall, ending early without drizzles or humidity like the eastern provinces of the Hoang Lien Son range. The summer is hot and characterized by unpredictable changes, influenced by dry and hot westerly winds. The province’s climate exhibits diverse variations based on terrain and seasons. Dien Bien also has the highest diurnal temperature range in the country.
Annual temperature
The average annual temperature ranges from 21°C to 23°C, with the lowest average temperatures usually occurring from December to February (ranging from 14°C to 18°C). The highest average temperatures are observed from April to September (25°C), primarily in areas below 500 meters in elevation. The average annual temperature has shown a gradual increase over the decades.
The temperature regime in Dien Bien vividly reflects the relationship between atmospheric circulation and geographical conditions. Due to its location behind the Hoang Lien Son mountain range, cold air masses moving towards Dien Bien must pass through the upstream of the Da River valley. During this journey, the cold air mass gradually loses its chilliness, resulting in warmer and drier winters compared to the Northeast region. However, due to the relatively enclosed terrain, whenever a strong cold front arrives, the cold air lingers for an extended period, causing prolonged cold spells lasting several days.
The record low temperature in Dien Bien was -4.2°C, recorded at 6 a.m. on January 25, 2016 (Pha Din station).

Annual rainfall
The average annual rainfall varies from 1350 mm to 2200 mm, distributed unevenly among different localities. In recent years, the total annual rainfall has significantly decreased, particularly from the 1970s to the 1980s. The rainy season typically starts in May and ends in September, earlier than in provinces at lower latitudes. The dry season lasts from October to April of the following year. The average annual humidity ranges from 77% to 90%. Dien Bien enjoys abundant sunshine, with approximately 1850 to 2150 hours per year and 115 to 215 hours per month. The months of June and July have the fewest sunny hours, while March, April, August, and September have the highest sunny hours.
Hydrological regime:
Dien Bien is rich in water resources with three major river systems: the Hong (Da) River system, the Me Kong River and the Ma River. The rivers in the province have steep slopes and many rapids, especially those in the Da River and Nam Rom River systems, making them suitable for hydroelectric development. The water quality is relatively high and less polluted.
Da River
The Da River in Dien Bien has five main tributaries: Nam Ma (63 km long), Nam Bum (36 km long), Nam Po (103 km long), Nam Muc (86 km long), and Nam Muoi (50 km long). The total area of the river basins is about 5300 km², accounting for 55% of the province’s natural area. The Da River flows through the districts of Muong Nhe, Muong Cha, Tua Chua, Tuan Giao, and the town of Muong Lay.
Ma River
As for the Ma River, it has two main tributaries: Nam Hua (62.5 km long) and Suoi Lu (39 km long). The total area of the river basins is 2550 km², making it the second-largest river system in the province.
Me Kong River system
On the other hand, the Me Kong River system has a smaller basin area of 1650 km² with two main branches: Nam Rom River and Nam Nua River. The Nam Rom River originates from Dien Bien district, passes through Dien Bien Phu City, and flows into Laos. The Nam Nua River originates from Muong Nha, flows from south to north, then changes direction from east to west, meeting the Nam Rom River in Dien Bien Phu before flowing into Laos.
The province has over 10 lakes and more than 1000 rivers and streams, distributed relatively evenly. Notable features include Pa Khoang Lake, Hua Pe hot spring, and Uva hot spring. The major concentration of groundwater sources lies in expansive valleys like those found in Dien Bien, Tua Chua, and Tuan Giao districts. Although significant groundwater reserves exist, only a few organizations have conducted exploratory drilling projects, and the exploitation of these reserves has not commenced yet.
Economy of Dien Bien Province:
In 2021, the Gross Regional Domestic Product (GRDP) of Dien Bien province reached 12,463.87 billion Vietnamese dong, a 6.01% increase compared to the previous year. The agricultural, forestry, and fisheries sector contributed 2,226.73 billion dong, a 4.31% increase. The industrial and construction sector reached 2,737.32 billion dong, an 11.10% increase. The service sector contributed 6,929.79 billion dong, a 4.64% increase. Product taxes, excluding subsidies, amounted to 570.03 billion dong, a 6.49% increase.
Economic growth:
In 2021, Dien Bien province experienced positive economic growth, with the Gross Regional Domestic Product (GRDP) reaching 12,463.87 billion VND, a 6.01% increase compared to the previous year. The agricultural, industrial, and service sectors contributed significantly to this growth. Additionally, the total GRDP based on current prices was 21,851.55 billion VND, showing a 7.18% increase. The province’s economic structure underwent slight changes, with a higher share in the industrial and construction sectors. The per capita GRDP also rose to 34.96 million VND per person per year.
Finance – Banking:
The banking sector has tightly managed and implemented synchronized and flexible policies, financial tools, and monetary regulations in compliance with government and central bank directives. It has ensured the stability and safety of credit institutions’ operations, while mobilizing and timely supplying capital for production, business activities, economic recovery, and development. The sector has prioritized credit for agriculture, rural areas, small and medium-sized enterprises, actively implementing support measures, and resolving difficulties for customers affected by the Covid-19 pandemic.
* Cash transactions:
The banking sector has met all cash payment and disbursement needs, promptly serving the province’s economic and social development. Commercial banks in the area have provided reliable cash withdrawal services at ATMs, maintaining sufficient cash circulation to meet the cash withdrawal demands of the people. Particularly during the Lunar New Year and holidays, no incidents occurred.
* Safety of cash reserves:
Bank in the area strictly comply with cash reserve management regulations, ensuring absolute safety of cash, valuable assets, and documents. Credit institutions have effectively carried out currency selection and classification to ensure the cleanliness of circulating currency, as well as implemented measures to ensure cash transaction operations under Covid-19 conditions.
* Capital mobilization:
The total credit capital mobilization as of December 31, 2021, reached 13,500 billion VND, a 10.6% increase compared to the same period last year, exceeding the plan by 2.4% (with savings deposits increasing by 13.88%). Banks in the area continue to promote and apply various flexible and market-adaptive forms of capital mobilization.
* Credit activities:
The total outstanding credit as of December 31, 2021, reached 19,300 billion VND, a 3.57% increase compared to the same period last year. Short-term loans accounted for 7,785 billion VND, a 5.92% increase, representing 40.3% of the total outstanding credit, while medium and long-term loans accounted for 11,515 billion VND, a 2.05% increase, representing 59.7% of the total outstanding credit. Non-performing loans stood at approximately 208 billion VND, accounting for 1.08% of the total outstanding credit.

Agriculture, forestry, aquaculture:
Agriculture:
In the province, crop cultivation in 2021 saw positive results with increased production compared to the previous year.
1. Annual crops:
– Rice cultivation: Increased by 2.71% compared to the previous year, surpassing the plan by 2.79%. The preliminary yield was 37.08 quintals per hectare, and the total rice production reached 199,507.44 tons, exceeding the plan by 5.66%.
– Corn cultivation: Decreased by 2.50% compared to the previous year, achieving 94.76% of the plan. The preliminary yield was 28.27 quintals per hectare, and the total production was 76,884.43 tons.
– Starchy tuber crops: Increased, with cassava growing by 7.33% and sweet potatoes by 11.79%. The total production of cassava reached 91,611.53 tons, and sweet potatoes reached 8,777.72 tons.
– Oilseed crops: Declined, with soybeans decreasing by 7.48% and peanuts by 1.95% due to various factors such as weather conditions and market prices.
– Vegetable, bean, and flower crops: Various vegetables increased by 5.37%, while bean cultivation decreased by 7.18%. The total vegetable production reached 82,174.28 tons.
Overall, annual crop production exceeded set targets, contributing to the province’s economic stability amid the challenges posed by the Covid-19 pandemic.
2. Perennial crops:
– Fruit trees: Increased by 22.20%, with mangoes, longan, and macca trees showing positive results in terms of yield and production.
– Rubber trees: Decreased slightly due to the liquidation of a small area. However, the harvested area and yield increased compared to the previous year.
– Coffee trees: Decreased by 25.42%, but the preliminary yield per hectare increased significantly.
– Tea bud trees: Remained unchanged, but the preliminary yield and total yield per hectare increased.
3. Pest and disease situation: The province took proactive measures to control pests and diseases, but unpredictable weather conditions affected crop yields and caused losses for farmers.
Forestry:
* Forest planting and management: According to preliminary reports, the province has planted a total of 1,211.46 hectares of new forests, an increase of 1,017.49 hectares compared to the previous year. This includes 948.70 hectares of productive forests (timber forests), an increase of 863.60 hectares from the official figures of the previous year, and 262.76 hectares of protective forests (timber forests), an increase of 153.89 hectares. The decentralized tree planting is also being implemented, with a total of 51,083 trees planted across the province.
* Forest protection: Forest protection has been given regular attention since the beginning of the year, and functional departments have provided enhanced guidance to local authorities in effectively managing state-owned forests and forest land. The allocated area for protected forests is 401,579.0 hectares, a 42.39% increase compared to the previous year. According to the report from the Forest Protection Department, there have been 319 violations of forest management regulations in the province. These include one forest fire covering an area of 0.08 hectares caused by local residents burning forests for shifting cultivation (occurred in Nam Po district), and 160 cases of illegal deforestation resulting in 26.98 hectares of forest damage caused by individuals clearing forests for cultivation. Additionally, there were 51 cases of illegal logging and 107 cases of illegal trading, transportation, storage, and possession of forest products. The authorities confiscated a total of 164.86 cubic meters of various types of timber. The total amount of fines collected during the year was 1.82 billion Vietnamese dong.
Aquaculture:
The province currently has 2,716.12 hectares of fishponds and aquaculture lakes, a 3.27% increase compared to the same period last year. Aquaculture in the province is mainly carried out using extensive and semi-intensive methods, with year-round harvesting on the same area (fish cultivation covers 2,714.67 hectares, a 3.28% increase). The model of cage fish farming in reservoirs continues to receive investment and expansion. In the month, there were a total of 255 fish cages with a volume of 36,392 cubic meters (88 cages in Dien Bien district, 59 cages in Tua Chua, 3 cages in Muong Cha, 101 cages in Dien Bien Phu city, and 4 cages in Muong Lay town).
The model of tank fish farming in Tuangiao district is still well maintained and developed, with 15,000 cubic meters of tanks for raising sturgeon and salmon (6,000 cubic meters for salmon and 9,000 cubic meters for sturgeon). Aquaculture facilities regularly monitor water levels and the aquaculture environment to ensure optimal growth and development of aquatic products, and there were no major outbreaks or diseases reported in the month.
Industry:
The estimated industrial production index in 2021 is projected to increase by 8.32% compared to 2020. In particular, the mining sector is expected to increase by 4.46%; the processing and manufacturing industry is expected to increase by 2.46%; the production and distribution of electricity is expected to increase by 21.57%; and the water supply, waste management, and wastewater treatment sector is expected to increase by 5.05%. In the secondary industrial sectors, several industries are anticipated to have high production indexes in 2021 compared to the previous year, contributing significantly to the overall industry growth. These include the production and distribution of electricity with a projected increase of 21.57%; beverage production with a projected increase of 11.64%; waste collection, treatment, and disposal activities with a projected increase of 8.52%; pre-cast metal products (excluding machinery and equipment) with a projected increase of 8.19%; other mining activities with a projected increase of 7.82%; food processing with a projected increase of 7.43%; repair, maintenance, and installation of machinery and equipment with a projected increase of 7.1%; and chemical production and chemical products with a projected increase of 6.31%. Additionally, some sectors are expected to have a decrease in production indexes in 2021 compared to the previous year, including the extraction of hard coal and brown coal with a projected decrease of 69.08%; metal ore mining with a projected decrease of 25.73%; production of non-metallic mineral products with a projected decrease of 9.4%; and leather production and related products with a projected decrease of 1.73%.
Key industrial products:
Some key industrial products in 2021 include 276,765 tons of cement, a 2.35% increase compared to the same period last year, achieving 83.87% of the plan; electricity production reaching 475.43 million KWh, a 20.67% increase, achieving 125.11% of the plan; 936,430 cubic meters of construction stone, an 8.77% increase compared to the previous year, surpassing the plan by 17.05%; 9.53 million cubic meters of produced water, a 3.03% increase, exceeding the plan by 5.89%; and waste collection services with a 7.50% increase, achieving 79.49% of the plan.

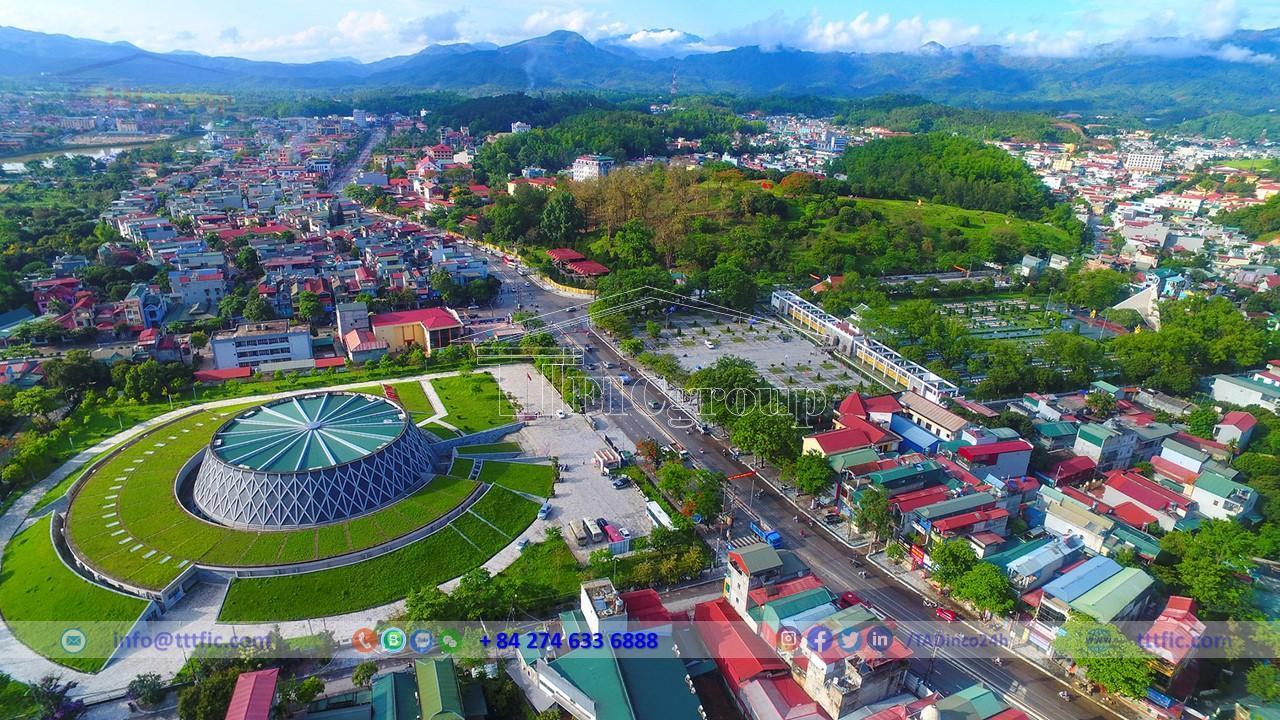
Social:
Residential:
As of 2021, the population of Dien Bien province is 625,100 people, with a population density of 66 people per square kilometer. Among them, the male population is 317,400 people and the female population is 307,700 people. The urban population is 95,000 people, while the rural population is 530,100 people. The natural population growth rate of Dien Bien from 2009 to 2019 is 2 ‰. In 2019, there are 134,273 households in Dien Bien, including 24,646 households in urban areas and 109,627 households in rural areas. The urbanization rate as of 2022 is 30%.
According to the 2019 population survey, Dien Bien province is home to 42 ethnic groups, including Thai, Mong, Kinh, Dao, Khơ Mú, Hà Nhì, Giáy, La Hủ, Lự, Hoa, Kháng, Mảng, Tày, Nùng, Mường, and others. Among them, the Mong ethnic group has the largest population with 228,279 people, accounting for 38.1% of the province’s total population. The Thai ethnic group ranks second with 213,714 people, accounting for 35.6% of the province’s population. The Kinh ethnic group has the third largest population with 104,061 people, representing 17.3% of the province’s population.
Healthcare:
The effective maintenance and implementation of healthcare activities and targeted healthcare programs have gradually improved the quality of medical services in Dien Bien province. The disease situation is stable, with no major outbreaks occurring. It is estimated that throughout the year, the total number of medical examinations will exceed 1,000,000 people, with 103,800 inpatient treatments and over 6,500 outpatient treatments. The bed occupancy rate reaches 112%. However, due to being a mountainous province, 90% of the population consists of ethnic minorities living mainly in remote highland areas. Therefore, healthcare and disease prevention still face many limitations and challenges.
Education:
In Dien Bien province, there are a total of 517 schools, including 333 primary and secondary schools, comprising 176 primary schools, 124 lower secondary schools, 21 upper secondary schools, 1 primary and 1 secondary school. Education quality has been steadily enhanced over time.. Educators continue to innovate teaching methods, fostering creativity and students’ interest in learning, while providing opportunities for students to showcase their abilities and potential. The proportion of qualified and above-standard teachers and educational administrators is increasing rapidly. However, there are still many difficulties in the educational activities in Dien Bien, including inadequate infrastructure and challenges in accessing schools.
The literacy rate in Dien Bien is 73.1%, with more males and urban residents being literate compared to females and rural areas.
Religion:
According to the 2019 statistics from the General Statistics Office, the province houses five different religions, totaling 60,668 followers. Protestantism is the largest religious group, boasting 57,920 followers, followed by Catholicism with 2,672 followers, and Buddhism with 73 followers. Additionally, there are two followers of Caodaism and one follower of Bửu Sơn Kỳ Hương. Notably, Dien Bien stands as one of the provinces in Northern Vietnam with the lowest Catholic population, constituting only 0.4% of the overall population. Conversely, it holds the highest number of Protestant followers in the region, exceeding 50,000 believers. The majority of the remaining population identifies as non-religious.




