Quang Binh province:
Quang Binh province, a coastal province located in the southern part of North Central Vietnam, captivates with its rich history and natural resources. This province is the site of the Gianh River, which historically separated Đàng Trong and Đàng Ngoài, as well as the Luỹ Thầy set up by the Nguyễn lords during the Trịnh–Nguyễn War.
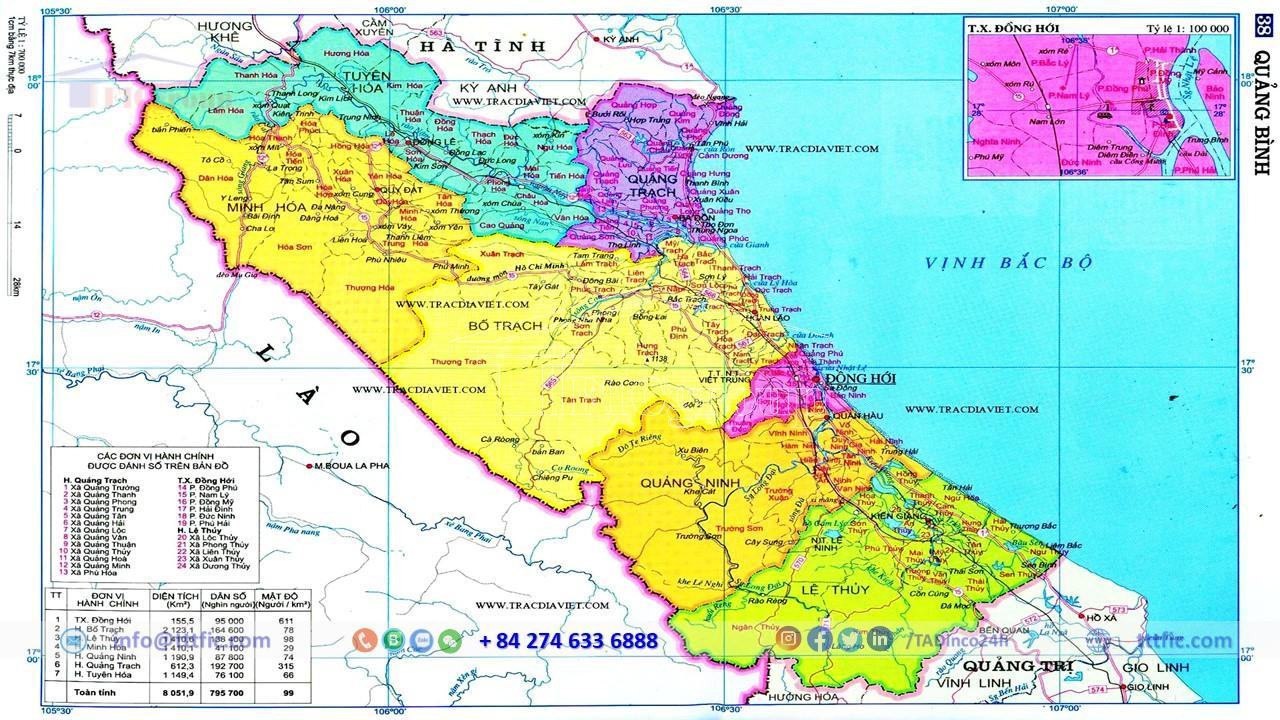
Administratively, Quang Binh houses 8 district-level divisions, which includes 6 districts, one city, and one town. These are further divided into 159 commune-level subdivisions – a total of 136 communes, 16 wards, and 7 towns. Thus, Quang Binh exhibits a dynamic and organized administrative structure.
Located in the North Central region of Vietnam, Quang Binh, with its total natural area of 8,065 km2 and a population of 895,430 as of 2019, is a significant player in the country’s regional development. The province’s strategic position makes it an excellent connection point to other localities within Vietnam and beyond, acting as a gateway to the world.
Indeed, Quang Binh boasts abundant natural resources and holds vast potential for tourism development. Its rich landscapes are the province’s pride, offering opportunities for both adventure and relaxation. Therefore, Quang Binh serves not just as a pivotal hub for transportation, but also as a major destination for travellers globally.
In conclusion, Quang Binh is a province that beautifully combines the charm of its historical past and the promise of its bright future. It is a region where nature, history, and culture converge, making it a compelling destination in Vietnam.
Geography of Quang Binh province:
Geographical location:
Situated between 16°55’ to 18°05’ north latitude and from 105°37’ to 107°00’ east longitude, Quang Binh Province spans a considerable distance, 500 km south of Hanoi and 267 km south of Da Nang, accessed via National Highway 1. This geographical location marks Quang Binh as a significant point of interest.
Adjacent to Ha Tinh Province in the north and bordering Quang Tri Province to the south, Quang Binh carves a unique profile in Vietnam’s map. Furthermore, it extends to the west, forming a border of 201.87 km with the provinces of Khammuane and Savannakhet in Laos. To the east, the province graces the magnificent East Sea.
The province’s geographic extremities are scattered across distinct points. The northernmost point is nestled in the Hương Hóa reserve forest, Tuyên Hóa district. The easternmost point resides in Tây Thôn village, Lệ Thủy district, whereas Trọng Hóa commune, Minh Hóa district, marks the westernmost point. The southernmost point is situated in Kim Thủy commune, Lệ Thủy district.
Quang Binh, sprawling over 8,065.3 km², housed 936,607 residents in 2018, marking a population density of 110 individuals per square kilometer. Its provincial capital is the vibrant city of Dong Hoi.
The province holds the unique distinction of being the narrowest in east-west dimension in Vietnam, with a minimal stretch of 50 km from the Laos border to the East Sea. It shares natural boundaries with the Hoanh Son Range in the north and the Truong Son Range in the west. The eastern edge offers a view of the East Sea, while the south shares a border with Quang Tri Province. With a considerable coastline of 116.04 km along the East Sea and a shared 201.87 km border with Laos to the west, Quang Binh is indeed a gem in Vietnam’s geographic profile.
Topographic:
Quang Binh’s terrain is narrow and steep, sloping from west to east. Its total area is 85% hilly and mountainous. It comprises distinct ecological zones: high mountains, hills and midlands, plains, and coastal sand dunes.
The terrain is characterized by narrowness and steep slopes, descending from west to east. Hills and mountains make up 85% of the total area, resulting in significant division. The western region is primarily high mountains of 1,000-1,500 meters, with Phi Co Phi peak being the highest at 2,017 meters. Following this is a region of low hills, distributed in an inverted bowl-like pattern. Along the coast, there are narrow plains. Finally, the coastal areas feature scythe or fan-shaped sand dunes.
Climate:
Quang Binh, nestled in a tropical monsoon area, is subject to the weather patterns of both Northern and Southern regions, and it showcases two pronounced seasons:
The wet season, which runs from September through March, sees an average yearly rainfall of 2,000 – 2,300mm, with the heaviest downpours in September, October, and November. The dry season, spanning from April until August, typically maintains average temperatures of 24°C – 25°C. June, July, and August emerge as the warmest months. Temperature averages of Dong Hoi city, the provincial capital of Quang Binh, throughout the year are taken into account too.
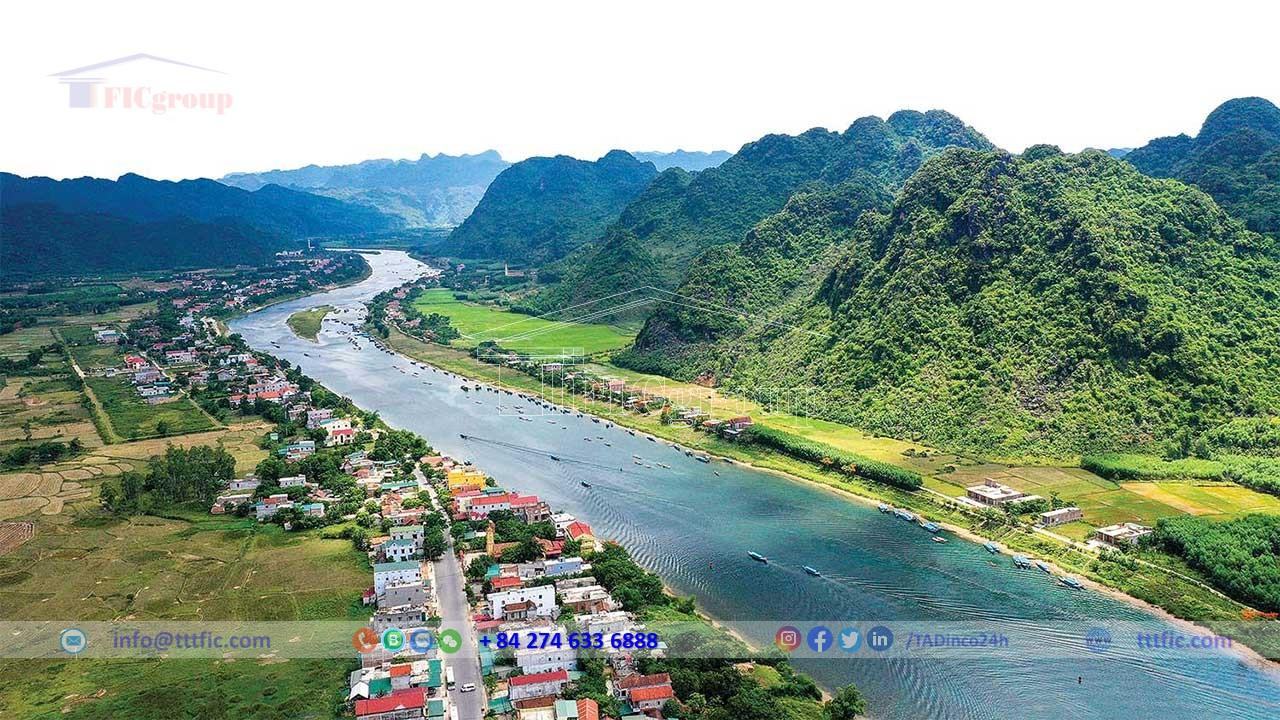
Rivers
Five major rivers traverse the province: the Gianh, the Roon, the Nhat Le (a confluence of the Kien Giang and Long Dai), the Ly Hoa, and the Dinh. They collectively discharge 4 billion cubic meters annually. Sourced from the Truong Son range, these rivers merge multiple basins and flow into the sea.
Land
As of 2007, Quang Binh’s natural area totaled 8,065.27 km² (806,527 ha), divided as follows:
Residential land: 4,946 ha Agricultural land: 71,381 ha Forestry land: 601,388 ha Special-use land: 23,936 ha Other non-agricultural land: 20,670 ha Unused land: 72,619 ha. The province’s land resources consist of two main systems: the plains contain alluvial soil, while the hills and mountains have lateritic soil, which comprises 15 types and major groups such as sandy soil, alluvial soil, and red and yellow soil groups. The red and yellow soil group, predominantly found in the western hilly and mountainous terrain, covers over 80% of the natural area. Sandy soil accounts for 5.9%, and alluvial soil makes up 2.8% of the area.
The flora and fauna
Quang Binh lies within the North Truong Son biodiversity region, home to diverse and unique plant and animal species with valuable genetic resources. The Karst Phong Nha – Ke Bang region represents the distinctive biodiversity of Quang Binh.
In terms of fauna, there are 493 species, including 67 mammals, 48 reptiles, 297 birds, and 61 fish. The province is home to several rare species, including Ha Tinh langur, bears, tigers, saola, large muntjac, white-tailed pheasant, black-crested pheasant, and quails.
Regarding plant diversity, the province boasts a forest area of 486,688 ha, including 588,582.92 ha of natural forest, 543,048.92 ha of planted forest, and 45,534.07 ha of forest yet to mature. Quang Binh harbors a wide range of plant species, with 138 families, 401 genera, and 640 different species. The forests of Quang Binh contain valuable timber such as ironwood, teak, ebony, rosewood, pine, and various bamboo species, along with other precious forest products. The province is known for its abundant timber reserves, currently estimated at 31 million m³.

Sea and island:
Quang Binh Province has a 116.04 km-long coastline (the third longest in the country) on the eastern side, with five river mouths, including two major ones and ports such as Nhat Le, Gianh, and Hon La. Hon La Bay covers an area of 4 km², with a depth of over 15 meters and protective islands such as Hon La, Hon Co, and Hon Chua, enabling 30,000 to 50,000-ton ships to dock without dredging. The spacious land area (over 400 hectares) is ideal for constructing industrial zones linked to deep-water seaports.
Quang Binh possesses a vast continental shelf and an expansive exclusive economic zone spanning over 20,000 km². Offshore, islands like Hon La, Hon Gio, Hon Nom, Hon Co, and Hon Chua have formed fishing grounds with a stock of 100,000 tons of diverse seafood.
The coastline, along with the significantly larger continental shelf, creates an extensive fishing ground in Quang Binh, with an estimated stock of 100,000 tons and rich biodiversity (1,650 species). This includes rare species such as lobsters, mantis shrimps, squids, cuttlefish, and coral. In the northern part of Quang Binh, there is a white coral reef covering an area of tens of hectares, providing precious raw materials for handicraft production and establishing an ecological habitat for coral reefs. This allows for the development of a comprehensive coastal economy.
In terms of aquaculture, with five river mouths, Quang Binh has a sizable water surface suitable for aquaculture, totaling 15,000 hectares. The salinity levels in these water bodies, ranging from 8-30%, and pH levels from 6.5-8, are highly favorable for shrimp and crab farming for export. The semi-diurnal tidal regime in coastal areas facilitates water exchange in shrimp and crab ponds.
Economy:
The estimated Gross Regional Domestic Product (GRDP) of the province in 2022 (at constant 2010 prices) reached over 27,720 billion VND, a 7.96% increase compared to 2021. The agricultural, forestry, and fishery sectors grew by 2.54%, contributing 6.18% to the overall GRDP; the industrial and construction sector grew by 11.41%, while the service sector grew by 8.57%. The scale of GRDP in 2022 (at current prices) exceeded 50,100 billion VND, with a per capita GRDP of 54.8 million VND.
As of December 15, 2022, the province had 769 newly established businesses, a 2.5% increase compared to the same period last year. The registered capital reached 11,980 billion VND, a growth of 11.8%, and the number of businesses returning to operation was 207, the same as the previous year.
The estimated value of the service sector’s production in 2022 increased by 9.34% compared to 2021. The total retail sales of goods reached 48,323 billion VND, a 14.4% increase over the previous year. Accommodation revenue in 2022 was estimated at 447.5 billion VND, five times higher than in 2021. The number of overnight tourists in 2022 reached 1.3 million, a 5.1-fold increase compared to the previous year, including 29.5 thousand international overnight visitors, a 4.7-fold increase compared to 2021.
The revenue from food services in 2022 was estimated at 4,115 billion VND, a 25.2% increase compared to 2021. The revenue from travel agencies reached 351.2 billion VND, five times higher than in 2021. The number of package tour tourists in 2022 was 541,022, a 5.1-fold increase compared to the previous year, including 26,130 international tourists, a 6.4-fold increase compared to the same period. The total state budget revenue in 2022 was estimated to exceed 8,000 billion VND, while the state budget expenditure was estimated to exceed 15,115 billion VND.

Social:
Residential:
According to the population census as of April 1, 2019, the population of Quang Binh reached 895,430 people. There are 24 ethnic groups living together in the province, but the majority are Kinh people, accounting for about 97%. The minority ethnic groups belong to two main groups, namely the Chut and Bru-Van Kieu, including the following ethnic groups: Khua, Ma Lieng, Ruc, Sach, Van Kieu, May, Arem, etc. They are concentrated in the mountainous districts of Tuyen Hoa and Minh Hoa, as well as some western communes of Bo Trach, Quang Ninh, and Le Thuy. The population distribution is uneven due to the narrow and steep terrain, with 60% living in rural areas and 30% in urban areas.
Quang Binh has an abundant labor force of 530,064 people, accounting for about 60.72% of the population. The male-to-female labor ratio is 265,206 to 264,858, respectively. As of the end of 2016, the quality of human resources in terms of education and training included 4 associate professors, 63 doctors, 69 specialists with a level II degree, 168 specialists with a level I degree, 2,015 masters, 30,653 people with a university degree, and 20,664 people with a college diploma or intermediate level. Trained labor accounted for 63.1% of the total labor force.
As of April 1, 2019, the province had 6 different religions with a total of 101,946 followers, with the largest being Catholicism with 101,246 followers, followed by Buddhism with 680 followers. The remaining religions, such as Protestantism, had 16 followers, while Islam had two followers. Hoa Hao Buddhism and Caodaism each had one follower.
Education:
Quang Binh province had 590 schools in the academic year 2017-2018, including 182 preschools, 209 primary schools, 147 lower secondary schools, 19 upper secondary schools, and 27 high schools. There were a total of 7,205 classrooms, with 5,146 solid classrooms and 1,940 semi-solid classrooms. The province employed 19,435 staff members, comprising management, teachers, and staff. The student population across all levels was 219,791, with 61,620 in preschool, 73,754 in primary school, 54,647 in lower secondary school, and 29,770 in upper secondary school.
Quang Binh achieved universal lower secondary education at level 1, with all 159 communes and towns meeting the standards and 154 surpassing higher-level standards. Additionally, 90 communes and towns achieved level 3 standards. The construction of national standard schools was emphasized, resulting in 325 schools meeting the standards.
In terms of academic achievements, Võ Nguyên Giáp High School excelled, with 36 out of 58 students in the National Excellent Student Competition receiving recognition. Nguyễn Thế Quỳnh, a student from the same school, won a Silver Medal at the Asian Physics Olympiad and represented Vietnam in the International Physics Olympiad, earning 4 gold medals and 1 silver medal.
Quang Binh province had 1 university, 4 colleges, and 2 vocational schools. Quang Binh University admitted 833 students out of 2,090 admissions slots for undergraduate and college programs.
Overall, Quang Binh province made significant progress in its education system, focusing on infrastructure development, academic excellence, and expanded opportunities for higher education.



