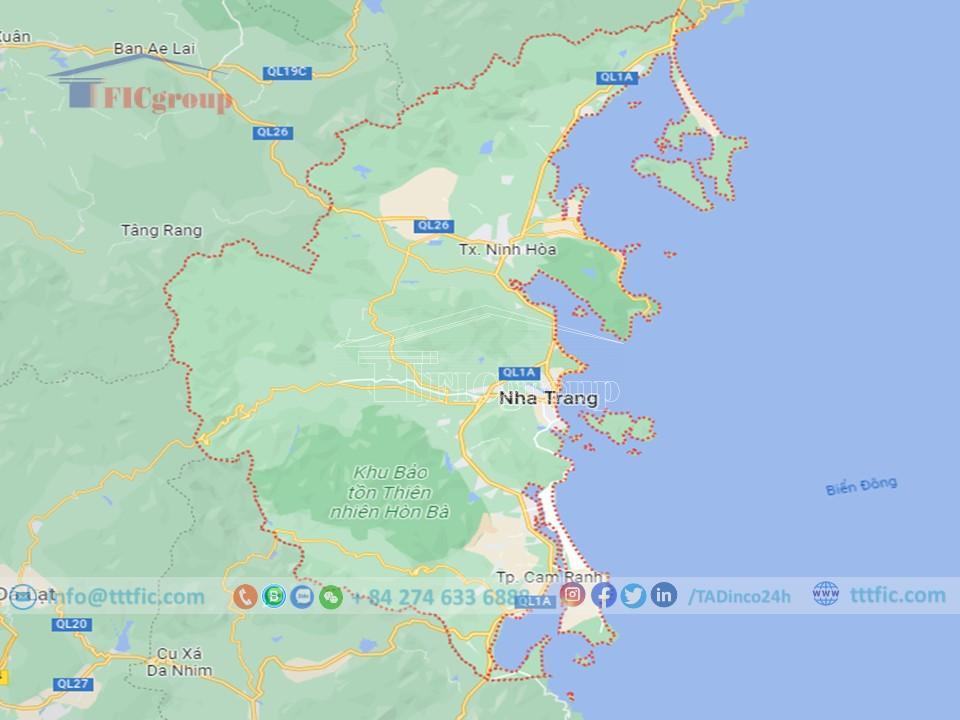
Overview of Khanh Hoa Province:
Khanh Hoa province is a coastal province located in the South Central Coast region of Vietnam. In 2018, it ranked as the 33rd most populous administrative unit in Vietnam, 24th in terms of Gross Regional Domestic Product (GRDP), 15th in terms of per capita GRDP, and 42nd in terms of GRDP growth rate. With a population of approximately 1,232,400, Khánh Hoà achieved a GRDP of 76,569 billion Vietnamese Dong (equivalent to 3,3250 billion USD), a per capita GRDP of 62.13 million Vietnamese Dong (equivalent to 2,698 USD), and a GRDP growth rate of 7.36%.
Khánh Hoà was historically part of the ancient land of Kauthara in the Champa Kingdom. In 1653, under the pretext of King Chiêm Thành being associated with Princess Bà Tấm and causing trouble for the Vietnamese people in Phú Yên, Lord Nguyễn Phúc Tần sent General Hùng Lộc to lead an army to conquer the Phan Rang region to Phú Yên. In 1832, King Minh Mạng established Khánh Hoà province based on the Bình Hòa district. After a merger in 1975, the National Assembly divided Phú Khánh province into two separate provinces, Phú Yên and Khánh Hoà, which remains the case until today.
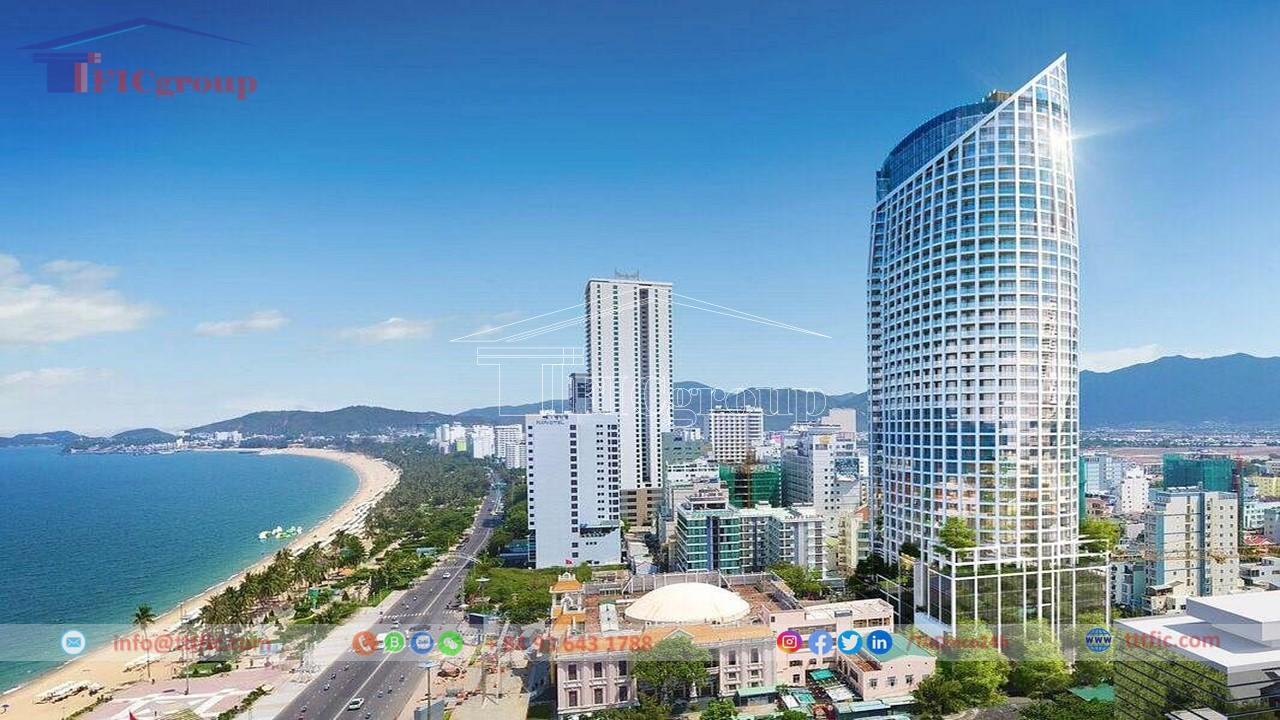
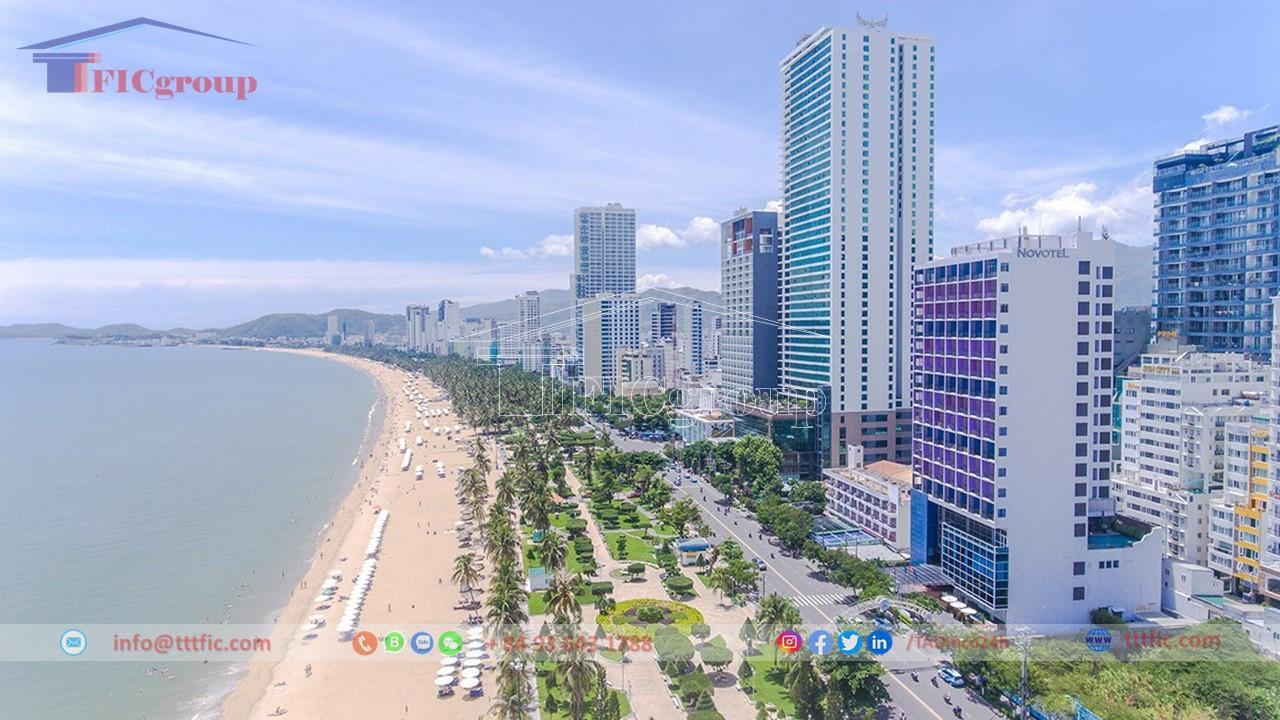
Khánh Hoà is known for its attractive tourist destinations such as the coastal city of Nha Trang, Nha Trang Bay, Hòn Mun Island, Cam Ranh beach resort, and the cultural heritage of Nha Trang Stone Church. The province also has a developed economy in sectors such as tourism, agriculture, seafood processing, and services.

Khanh-Hoa-Province-TTTFICgroup
Natural condition of Ninh Thuan province:
Geographical location:
Khánh Hòa is a coastal province in Vietnam’s South Central Coast region. It borders Phú Yên to the north, Đắk Lắk to the west, Ninh Thuận to the south, Lâm Đồng to the southwest, and the East Sea to the east.
The province’s capital is Nha Trang, located 443 km south of Ho Chi Minh City, 531 km north of Đà Nẵng, and 1,280 km north of Hanoi along National Highway 1.
Khánh Hòa covers an area of 5,197 km², stretching approximately 150 km in length and having a maximum width of about 90 km. There is a disputed area of 9,300 hectares between Ea Trang commune in Đắk Lắk province and Ninh Tây commune in Ninh Hòa town of Khánh Hòa province.
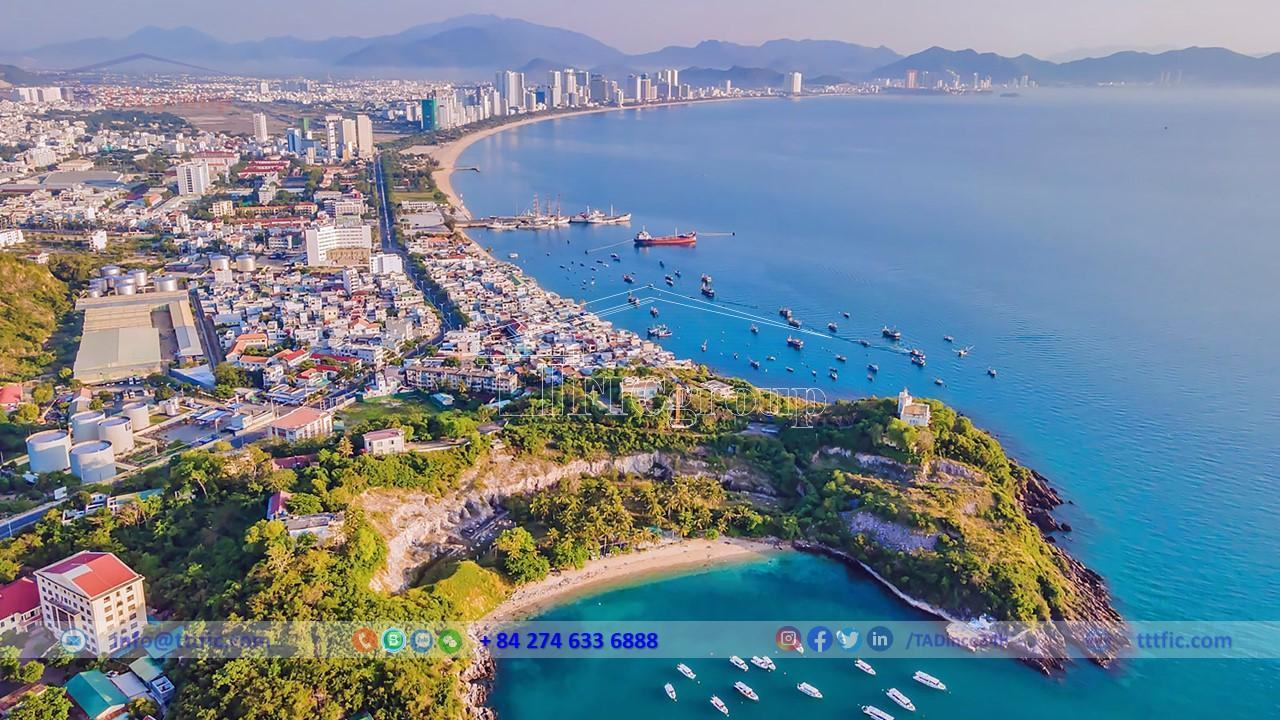
The province holds strategic significance due to its geographical location near international maritime routes. It includes the Trường Sa archipelago district, the Cam Ranh port, and serves as a gateway to the East Sea.
Khánh Hòa features a long coastline, numerous islands, and beautiful bays such as Vân Phong, Nha Trang, and Cam Ranh. It has a mild climate with an average temperature of 26°C and over 300 sunny days per year. The province is also known for its historical and cultural landmarks.
In addition, Khánh Hòa is rich in diverse natural resources, particularly marine resources, including valuable seafood for exploitation, aquaculture, processing, and export. It is a significant source of special ingredients for nutritional and medicinal products, such as bird’s nests, for exportation and production.

Khanh-Hoa-Province-TTTFICgroup
Topography:
Khánh Hòa is a province located near the Trường Sơn mountain range, primarily consisting of mountains with a narrow lowland area of about 400 km². The lowland is divided by mountain ranges that stretch from the land to the sea, resulting in numerous mountain passes throughout the province.
Land:
The province has a relatively high topography, with an average elevation of about 60 meters above sea level. The mountainous areas in Khánh Hòa are diverse, with some peaks reaching over 1,000 meters. In the northern and northwestern parts, there are high mountains such as Hòn Giữ, Hòn Ngang, and Hòn Giúp. The southern and southwestern regions have a wide mountainous area, including peaks over 1,500 meters, with Đỉnh Hòn Giao being the highest peak at 2,062 meters.
The province’s lowland areas are small and fragmented, divided by mountain ranges that reach the coast. Due to the mountainous terrain, the sedimentation process is not favorable for agricultural development. Notable lowland areas in Khánh Hòa include the Nha Trang – Diên Khánh lowland and the Ninh Hòa lowland, both formed by alluvial deposits from rivers. Additionally, there are two narrow lowland areas called Vạn Ninh and Cam Ranh near the coast, along with small cultivated areas in the valleys of the mountainous districts of Khánh Sơn and Khánh Vĩnh.

Khanh-Hoa-Province-TTTFICgroup
Coast and coastal sea:
Khánh Hòa boasts a beautiful coastline of approximately 385 km, with many estuaries, lagoons, bays, and about 200 islands along the coast. Prominent bays include Đại Lãnh, Vân Phong, Hòn Khói, Nha Phu, Nha Trang (Cù Huân), and Cam Ranh. Among them, Cam Ranh Bay stands out with its favorable natural conditions, serving as a significant seaport. Khánh Hòa also includes the Trường Sa archipelago with its coral islands, such as Ba Bình Island, Thuyền Chài reef, and other submerged sandbars.
Overall, Khánh Hòa’s topography is characterized by its mountainous regions, narrow lowlands divided by mountains, a beautiful coastline, and coral islands in the Trường Sa archipelago.
Geology – resources:
Khánh Hòa’s geological structure primarily consists of granite, ryolite, dacite, and various sedimentary rocks. The province’s land formation dates back to the ancient Kom Tom block, emerging from the sea approximately 570 million years ago. The physical and chemical weathering processes on the granite and ryolite have created unique and diverse natural landscapes in Khánh Hòa.
The province is rich in mineral resources such as mud coal, kaolin, fireclay, gold-bearing minerals, glass sand, coral, granite, ilmenite ore, and mineral water. These resources are utilized for construction materials and industrial purposes. Additionally, Khánh Hòa has abundant marine resources, including seaweed, marine plants, and a large quantity of seafood, which support the seafood processing industry. The favorable conditions also enable the exploitation of marine organisms and aquaculture.
Overall, Khánh Hòa possesses diverse geological formations and abundant mineral and marine resources, contributing to its renowned natural beauty.
Climate:
Khánh Hòa is a coastal province in the South Central Coast region of Vietnam, characterized by a tropical savanna climate. The province experiences unique climate variations with distinct characteristics. Compared to the northern provinces from Đèo Cả to Ghềnh Đá Bạc in the south, Khánh Hòa has a relatively mild climate influenced by its proximity to the ocean. It typically has two distinct seasons: a short rainy season from mid-September to mid-December, concentrated in October and November with over 50% of the annual rainfall, and the remaining months are sunny, with an average of 2,600 hours of sunshine per year. The average annual temperature in Khánh Hòa is around 26.7°C, with the mountain peak of Hòn Bà (30 km from Nha Trang) having a climate similar to Đà Lạt. The relative humidity is approximately 80.5%.
From January to August, it can be considered the dry season, with gradually changing weather. In the early months of the season, the weather is cool, with temperatures ranging from 17-25°C, but from May to August, it becomes hot, with temperatures reaching up to 34°C in Nha Trang and 37-38°C in Cam Ranh. September to December is considered the rainy season, with temperatures ranging from 20-27°C in Nha Trang and 20-26°C in Cam Ranh. Khánh Hòa is not prone to frequent typhoons, with an average of only about 0.82 typhoons making landfall per year, compared to the national average of 3.74 typhoons. Recent years have seen typhoons deviating southward or dissipating before reaching the province’s coast. However, due to the steep slopes of rivers and streams, heavy rainfall during typhoons can cause rapid flooding, while storm surges and high tides impede the drainage of water into the sea, often leading to flooding.
River:
Khánh Hòa has a network of rivers with approximately 40 rivers flowing from the mountainous areas in the west of the province to the east, forming a dense river distribution. Along the coastline, there is a river mouth approximately every 5-7 km.
Although the general flow direction of the rivers is west to east, depending on the topography or local geographical features, the rivers can meander in different directions before reaching the East Sea. Particularly, the Tô Hạp River, originating from the western mountain range of Khánh Sơn district, flows through Sơn Trung, Sơn Bình, Sơn Hiệp, Sơn Lâm, Thành Sơn, and then flows westward to Ninh Thuận. This is the only river in the province that flows upstream to the west. The two largest rivers in the province are the Cái River (Nha Trang) and the Dinh River. The Cái River is 79 km long, originating from Mount Gia Lê at an elevation of 1,812 m, flowing through Khánh Vĩnh, Diên Khánh, Nha Trang, and finally into the sea through Cửa Bé (Tiểu Cù Huân) and Cửa Lớn (Đại Cù Huân). The Dinh River originates from the Chư H’Mư mountainous region (with a peak at 2,051 m) in the Vọng Phu range, with a total basin area of 985 km². It flows through Ninh Hòa town and empties into the Nha Phu lagoon.

Khanh-Hoa-Province-TTTFICgroup
Economy of Khanh Hoa Province:
In 2022, Khánh Hòa province’s gross regional domestic product (GRDP) reached 54,505.2 billion VND, marking a remarkable growth of 20.7% compared to 2021. This outstanding growth rate positioned Khánh Hòa as the province with the highest GRDP growth rate in the country.. The economic recovery contributed to this growth, with the service sector increasing by 25.46%, the industrial and construction sector by 24.61%, and the agricultural, forestry, and fisheries sector by 2.49%.
The agricultural sector saw a growth of 1.31%, primarily affected by unfavorable weather conditions and increased production costs. The industrial and construction sector had a significant increase of 21.29%, while the construction sector contributed a growth rate of 31.47%. The service sector, which has the highest proportion in the GRDP, showed strong recovery with a growth rate of 25.46%. Activities such as tourism, trade, and transportation experienced significant growth, contributing to the overall economic growth.
Khánh Hòa’s GRDP ranked 31st out of 63 provinces and 6th among the 14 provinces in the North Central and Central Coastal regions. The economic structure consisted of 11.2% in agriculture, forestry, and fisheries, 32.39% in industry and construction, 46.53% in services, and 9.88% in tax minus subsidies on products. The per capita GRDP reached 76.54 million VND, an increase of 22.34% compared to 2021. Labor productivity was estimated at 147.18 million VND per labor, a growth of 11.59% compared to the previous year.
Agriculture, forestry and fishery production:
Agriculture:
Crop:
In Khanh Hoa province, the total cultivated area from the 2021-2022 crop to December 15, 2022, was 67,977.9 hectares, accounting for 95.95% of the plan. The main crops were food crops, with rice covering 43,259.8 hectares (95.64%) and maize covering 5,189.7 hectares (96.25%). Tuberous crops occupied 3,151.4 hectares (100.17%), food crops covered 5,002.2 hectares (91.65%), and annual industrial crops occupied 9,752 hectares (83.9%). Compared to the previous year, the total cultivated area decreased by 4.89%, mainly in food crops.
The province’s grain output in 2022 was 267,788.7 tons, with maize accounting for 11,181.3 tons (a decrease of 16.7 tons) and rice accounting for 256,607.4 tons (a decrease of 15,802.1 tons). The decrease in output was attributed to reduced cultivated area and average yield. The Winter-Spring rice crop decreased by 6.85% with an average yield of 64.61 kg/ha, while the Summer-Autumn rice crop increased by 0.26% with an average yield of 59.48 kg/ha. Unfavorable weather conditions and lower prices affected perennial crop production.
The existing cultivated area in 2022 was 23,273.2 hectares, slightly lower than the previous year. Fruit trees accounted for 17,633.8 hectares (an increase of 1.41%), while oil-bearing fruit trees decreased by 5.75%. Other perennial crops also experienced a decrease in cultivated area. Some fruit crops saw an increase in production due to better harvesting conditions, while others faced reduced yield and output due to adverse weather and decreased cultivated area.
Breed:
Livestock and poultry farming in Khanh Hoa province continued to develop steadily. The number of herds in poultry and pig farms is growing well, and the supply meets the increasing demand of people during Christmas, New Year, and Lunar New Year in 2023. As of the end of December 2022, there were 3,975 buffaloes, an increase of 1.77% compared to the previous year; 75,650 cows, a 1.1% increase due to good control of contagious bovine dermatitis; 287,000 pigs, a 7.35% increase due to the expansion of pig farms and high consumer demand in the later months; 3,194.8 thousand poultry (including 2,367.1 thousand chickens), a 5.86% increase.
The output of live meat in 2022 saw increases compared to 2021: pork increased by 18.68% to 27,997 tons, buffalo meat increased by 4.09% to 242.1 tons, beef increased by 3.58% to 4,062.1 tons, and poultry meat increased by 10.2% to 8,663.1 tons (including chicken meat, which increased by 13.44%). The production of poultry eggs also saw a slight increase. The disease situation in livestock and poultry herds is under control, and measures have been taken to ensure food hygiene, consumer safety, and environmental protection.
In 2022, outbreaks of African swine fever occurred in several villages of Nha Trang city, Cam Lam district, Van Ninh district, Dien Khanh district, and Khanh Vinh district. Authorities took prompt action to cull the affected herds. Contagious bovine dermatitis was identified in four villages, leading to the death of two calves. Appropriate measures were implemented to handle and dispose of the affected animals.
Forest:
In 2022, forestry production focused on forest care, regeneration, and protection, with an emphasis on concentrated reforestation, scattered tree planting, and new planting to maintain forest cover, protect water sources, prevent erosion and ensure ecological environments. The current weather conditions in the province, with rainfall, allow for the implementation of new reforestation and continued scattered tree planting. In December 2022, the new planted forest area reached 122.9 hectares, a 9.7% increase compared to the previous year. However, the number of scattered trees decreased by 28.16% due to earlier planting activities. Overall, forest development in the province in 2022 reached 2,858.6 hectares, a 3.07% increase from 2021.
The volume of timber extraction in December 2022 increased by 0.6% compared to the same period last year, reaching 8,019.8 cubic meters. Firewood production also increased by 0.7% to 4,047.8 stere. In the fourth quarter of 2022, timber extraction from newly planted forests reached 19,923.8 cubic meters, a 2.49% increase from the previous year, while firewood extraction decreased by 2.94% to 7,958.8 stere. Overall, timber extraction in 2022 reached 77,182.6 cubic meters, a 4.5% increase from 2021, due to high demand and prices for timber used in wood chip production. Firewood extraction reached 20,432 stere, a 2% increase due to the expanded timber extraction area.
The provincial authorities paid close attention to reforestation, forest care, management, and fire prevention. Authorities implemented effective fire prevention plans and conducted public awareness campaigns to promote compliance with forest protection and fire prevention regulations. In December 2022, one incident of forest destruction occurred, resulting in a damage area of 0.18 hectares, but no forest fires were reported. Throughout the year 2022, the province recorded a total of 33 forest destruction incidents, causing a damage area of 24.67 hectares.
Aquaculture
Aquaculture production has developed steadily, with favorable weather conditions and an increase in seafood exports. Total seafood production in 2022 increased by 3.13% compared to 2021. In December 2022, the total seafood production reached 5,186.9 tons, a 3.58% increase compared to the same period last year. Fish production decreased by 2.47% to 3,818.6 tons, while shrimp production increased by 13.97% to 440.3 tons, and other seafood production increased by 31.47% to 928 tons. In December 2022, harvested seafood reached 3,881.3 tons, a 3.33% increase compared to the same period last year. Marine seafood harvest amounted to 3,875.4 tons (a 3.41% increase), while inland seafood harvest amounted to 5.8 tons (a decrease of 30.88% due to pollution and excessive fishing). Aquaculture production reached 1,305.6 tons, a 4.33% increase. Fish production in aquaculture decreased by 5.92% to 643.5 tons, while shrimp production increased by 29.81% to 407 tons, and other seafood production increased by 0.48% to 255.1 tons. Cumulative seafood production in 2022 was 114,829.2 tons, a 3.13% increase compared to 2021. Harvested seafood reached 97,669.5 tons (a 1.76% increase), with 97,553.4 tons from marine sources (a 1.77% increase) and 116.1 tons from inland sources (a 3.13% decrease). Aquaculture production reached 17,159.8 tons, an 11.63% increase, with 9,113.4 tons of fish (a 17.74% increase), 4,345 tons of shrimp (a 6.11% increase), and 3,701.4 tons of other seafood (a 4.65% increase).
Industry:
Industrial production in the province continued to grow, with key industries contributing to a 21.7% increase in industrial production in 2022 compared to 2021. In December 2022, the industrial production index increased by 2.01% compared to the previous month and 7.95% compared to the same period last year.
The processing and manufacturing industry increased by 2.03% and 7.18%, while the production and distribution of electricity, gas, hot water, steam, and air conditioning decreased by 0.59% and increased by 15.69%.
The water supply and waste treatment industry increased by 11.1% and 14.3%, and the mining industry increased by 1.23% but decreased by 7.5%.
In 2022, the industrial production index increased by 21.7% compared to 2021. Major industries such as manufacturing and processing increased by 22.7%, electricity, gas, water, and air conditioning increased by 20.65%, while the mining industry decreased by 4.26%.
The production of transportation vehicles increased by 54.18%, textiles increased by 48.51%, pharmaceuticals increased by 43.23%, non-metallic mineral products increased by 39.98%, and paper and paper products increased by 28%. Overall, the consumption index of the manufacturing industry increased by 12.17% in 2022. However, some industries experienced a decrease in consumption, such as the wood processing industry and the production of straw, grass, and woven materials. The inventory index of the processing and manufacturing industry decreased by 0.6% compared to the previous year, with a decrease in clothing, paper products, beverages, and tobacco production. The workforce in industrial enterprises increased by 0.56% in December 2022 compared to the previous month and 0.39% compared to the same period last year.
Overall, the number of workers in state-owned enterprises and foreign-invested enterprises decreased, while the number of workers in non-state-owned enterprises increased.
Tourism
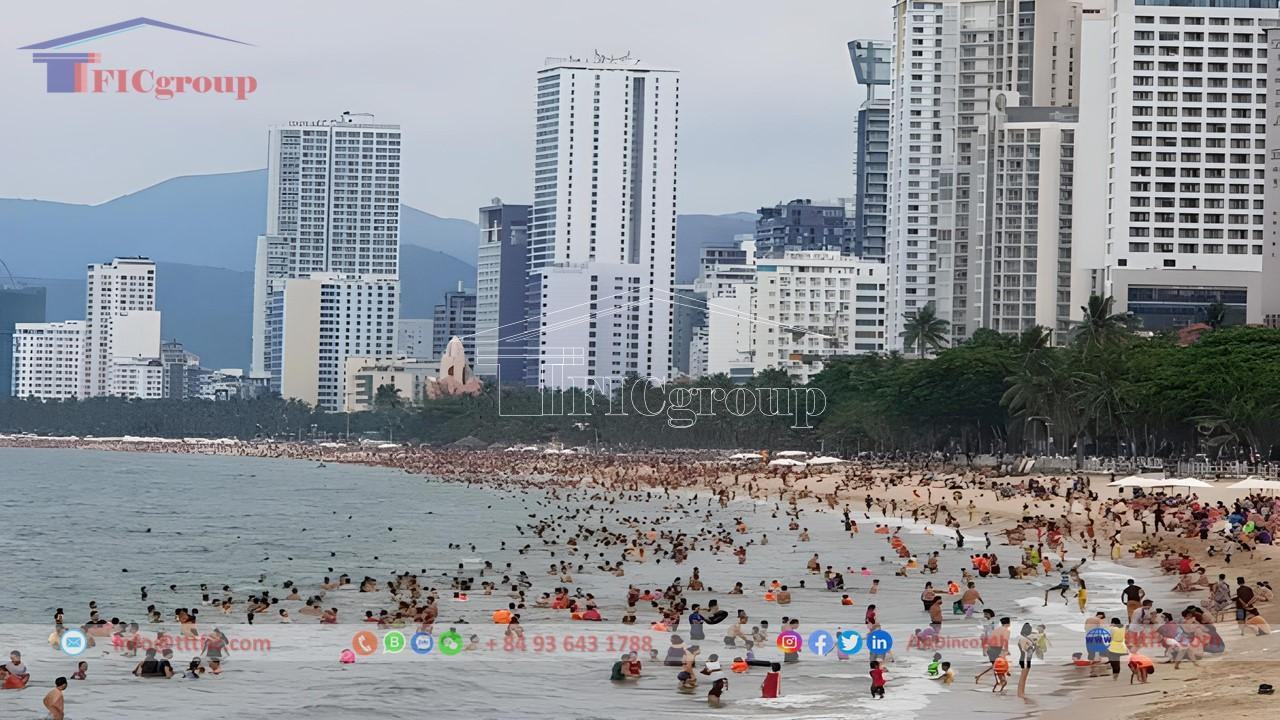
Due to heavy rain in the last months of the year, domestic tourism demand decreased significantly, but international visitors continued to increase, contributing to a tourism revenue of 1,033.8 billion VND in December 2022, up 4.92% compared to the previous month. The number of overnight visitors decreased by 4.59% to 152 thousand, while the number of visitor days increased by 1.53% to 410 thousand.
In the fourth quarter of 2022, tourism revenue reached 3,051.4 billion VND, a decrease of 41.74% compared to the third quarter of 2022 but 6.73 times higher than the same period last year. The number of overnight visitors decreased by 53.95% to 478.6 thousand, while the number of visitor days decreased by 49.32% to 1,228.9 thousand. South Korea became the largest international market for Khanh Hoa tourism due to the temporary closure of China and Russia. Vietnam Airlines announced the resumption of flights between Cam Ranh and Incheon, South Korea, with a frequency of 7 flights per week from November 30, 2022. In 2022, all tourism indicators exceeded the set targets and showed significant growth compared to 2021. Tourism revenue reached 13,843.8 billion VND, 2,566 thousand overnight visitors, and 6,158.7 thousand visitor days. International visitors accounted for 275.3 thousand and 1,252.4 thousand visitor days, respectively.

Khanh-Hoa-Province-TTTFICgroup
Social:
Residential:
Population:
According to the survey conducted on April 1, 2019, the population of Khanh Hoa province was 1,231,107 people, with a population density of 225 people/km². The male population accounted for 49.75% (612,513 people), and the female population accounted for 50.35% (618,594 people). The average population growth rate from 2009 to 2019 was 0.62%, and the gender ratio was 97.9%. In 2019, Khanh Hoa had 520,008 people living in urban areas (42.2% of the total population) and 711,099 people living in rural areas (57.8%). The urbanization rate reached 65% by the end of 2022.
The population distribution in Khanh Hoa is uneven. The most densely populated area is Nha Trang city, which accounts for one-third of the total population and serves as the political, economic, and cultural center of the province. Dien Khanh district and Cam Ranh city also have relatively high population densities (around 400 people/km²). Ninh Hoa town and the remaining districts in the delta have a population density similar to the provincial average (around 200 people/km²), while the mountainous districts have relatively low population densities, with Khanh Son (62 people/km²) and Khanh Vinh (29 people/km²). The district with the lowest population density in the province is Truong Sa island district (0.39 people/km²). According to the statistics from the General Statistics Office of Vietnam in 2010, there were approximately 519,600 people living in urban areas and 648,100 people living in rural areas.
In terms of age, in 2009, the entire province had 526,061 people under 25 years old (45% of the population), 450,393 people aged 25 to 50 (39% of the population), and 183,150 people over 50 years old (16% of the population).
Ethnic:
Currently, there are 32 ethnic groups living in Khanh Hoa province. The Kinh ethnic group has the largest population of 1,095,981 people in Khanh Hoa province, with distribution throughout the districts, towns, and cities, but mostly concentrated in the delta regions, cities, towns, and townships.
The largest ethnic minority group is the Raglai people, with 45,915 people mainly residing in Khanh Son and Khanh Vinh districts, as well as some mountainous communes in Dien Khanh, Cam Lam, and Cam Ranh city, in their villages (palay).
In the areas bordering Lam Dong and Dak Lak provinces, there are approximately 4,778 Co Ho people and 3,396 Ede people living. The Hoa ethnic group has around 3,034 people, mainly concentrated in Nha Trang city (around 2,000 people), Ninh Hoa town, and the eastern communes of Dien Khanh district. Another significant minority group is the Tày people (1,704) and Nung people (1,058), who migrated from northern provinces during the migration in 1954 and have been living mainly in Khanh Vinh district. Besides these major groups, there are other ethnic groups that make up a very small minority in the population, such as the Muong, Thai, Cham, Khmer, and Tho. The Cham people are indigenous inhabitants of Khanh Hoa. However, due to historical circumstances, Cham people in Khanh Hoa gradually moved to southern provinces since the mid-17th century. Therefore, nowadays, there are only about 290 Cham people in Khanh Hoa.
In the city of Nha Trang, there are also some groups of foreigners living and working regularly in recent years, and a few of them have settled long-term and obtained Vietnamese citizenship.
Religion:
According to the report from the General Statistics Office of Vietnam, during the population census in 2019, Khanh Hoa province had 265,316 individuals who identified themselves as having religious beliefs. The largest religious group was Catholicism with 132,992 followers, followed by Buddhism with 100,560 followers. Other religious affiliations included Protestantism with 24,500 followers, Caodaism with 6,819 followers, Hoa Hao Buddhism with 284 followers, and smaller numbers of Muslims (94), Baha’i (13), Tinh do cu si Phat hoi Viet Nam (17), and Minh Su Dao (12). Buddhism was most concentrated in Nha Trang (50.4%) and Dien Khanh, Catholicism was more prominent in Cam Lam, and Caodaism was concentrated in Cam Ranh. Protestantism was more prevalent in Khanh Son and Khanh Vinh. Hoa Hao Buddhism was mainly distributed in Ninh Ich commune.
Education – Healthcare:
Education:
During the French colonial period, Khanh Hoa province established scientific research institutions, including the Pasteur Institute of Nha Trang and the Indochina Fisheries Department, focusing on epidemiology, hygiene, and marine research.
Over time, the scientific field expanded to applied sciences to support the province’s economic development. Notable research projects in Khanh Hoa include the conservation of agarwood and ky nam, swiftlet preservation and cultivation, and aquaculture studies. Education in Khanh Hoa was limited before the Nguyen dynasty, but schools were established during the reign of King Gia Long. However, students had to travel to other provinces for higher education until the opening of Kim Yen Private High School in 1936. Nha Trang High School was established in 1947 and later upgraded to Vo Tanh High School. Since then, Khanh Hoa has offered education at various levels, culminating in the establishment of Duyen Hai Community College in 1971 and the relocation of Nha Trang Fisheries University. Currently, Khanh Hoa provides comprehensive education to cater to students in the province.
Healthcare:
Khanh Hoa province has a highly developed healthcare system in the South Central Coast region. Nha Trang is recognized as one of the three medical centers in the region, according to Decision 1047/QD-BYT by the Ministry of Health. As of June 30, 2017, the province had a public doctor-to-population ratio of 6.83 per 10,000 people, with 29.5 beds per 10,000 people. The prevalence of mild malnutrition in children under 5 years old in Khanh Hoa was 8.86% (targeted at 9%), and the health insurance coverage rate reached 81.93%.
Investments in the development of the healthcare infrastructure at the grassroots level have alleviated the burden on higher-level hospitals and improved access to healthcare for residents. Currently, 137 out of 140 communes have commune health stations, and all administrative units at the district level have district-level hospitals. The construction of new district-level hospitals has met the basic healthcare needs of the population. Khanh Hoa General Hospital is a Grade I hospital and one of the ten regional general hospitals in the country.