Tra Vinh province
Tra Vinh province is located in the southwestern region of Vietnam, with an area of about 2,295 square kilometers and a population of around 1.1 million people (in 2021). The province’s economy is mainly based on agriculture, particularly the cultivation of fruit trees such as mango, pomelo, coconut, and rice. Additionally, tourism and seafood processing also contribute to the province’s economy.
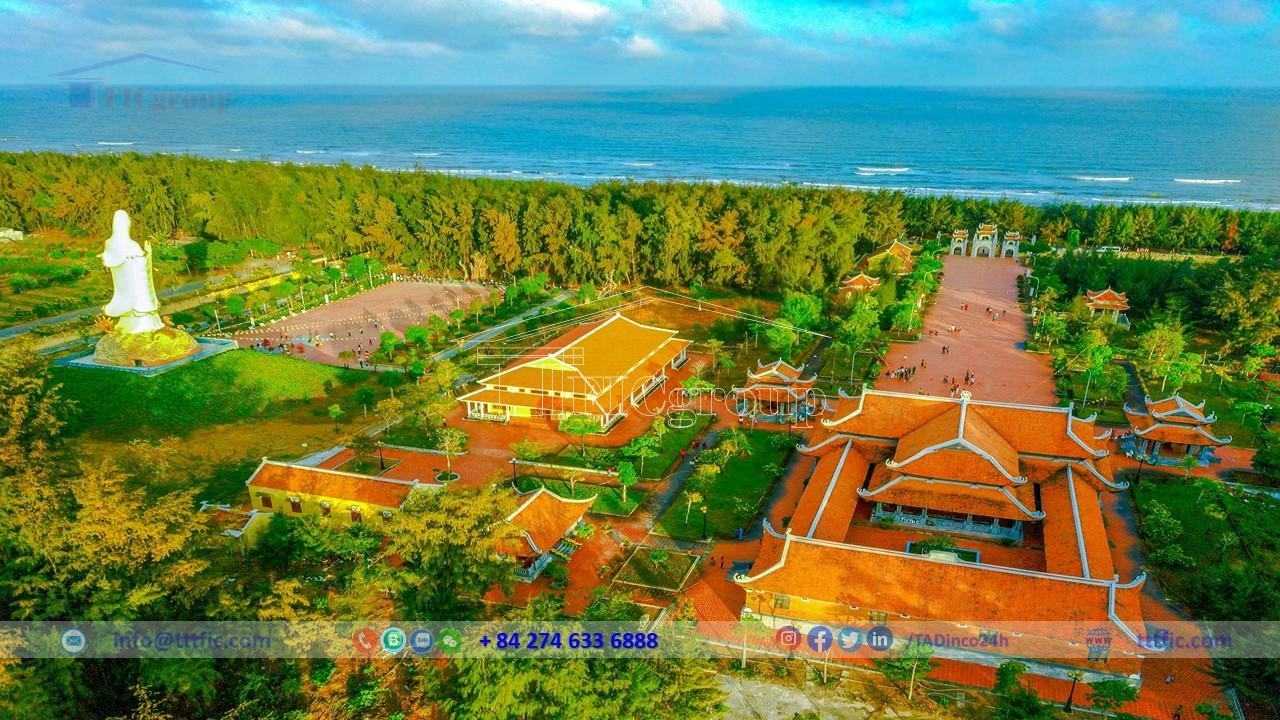
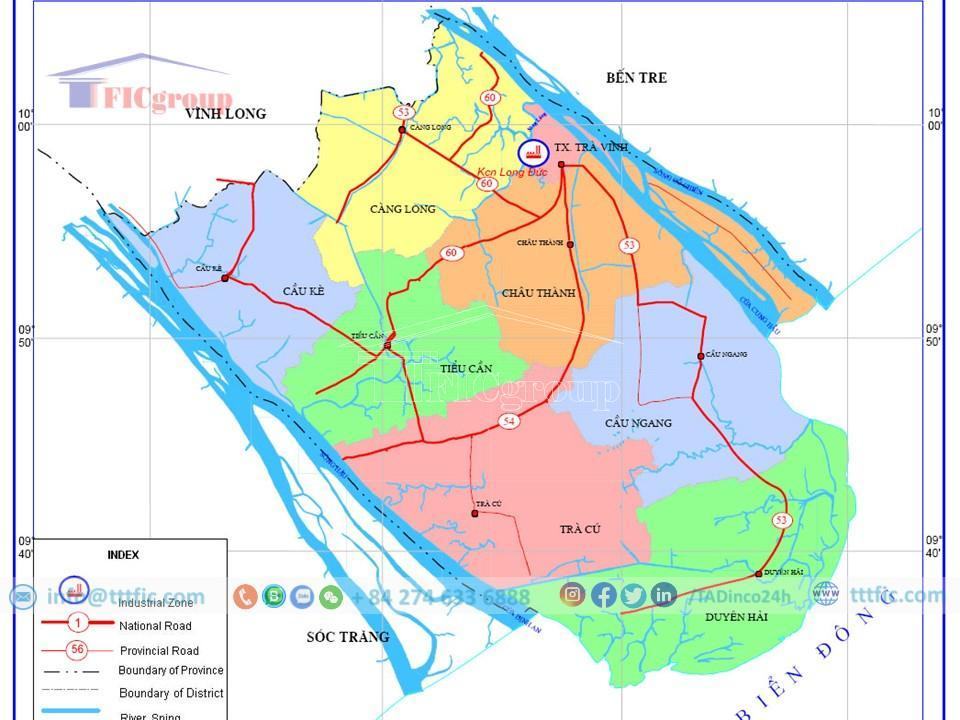
Tra Vinh province has many unique cultural and architectural heritage sites, such as Ang Pagoda, Cau Pagoda, Ba Diem Pottery Village, Ngoc Tuyen Candle Village, and weaving villages. The province also has many universities, colleges, and important transportation routes such as National Highways 53, 54, and 60, the Ho Chi Minh City – Trung Luong – My Thuan Expressway, and the Saigon – Ca Mau Railway. Tra Vinh province also has many shopping centers, stores, traditional markets, and night markets.
Natural Condition of Tra Vinh province
Location:
Tra Vinh is a province in the Mekong Delta, located between latitudes 9°31’46” to 10°4’5″ North and longitudes 105°57’16” to 106°36’04” East. From Ho Chi Minh City, go by Highway 53 through Vinh Long province about 200km or by Highway 60 through Ben Tre province about 130km. The province borders the East Sea to the east, Vinh Long to the west, Soc Trang to the Hau River to the south, and Ben Tre to the Co Chien River to the north. Waterway traffic is convenient because it is surrounded by Tien and Hau rivers.
Topographic:
Tra Vinh has mainly flat terrain with an altitude of about 1m above sea level. This area has many sand dunes running parallel to the coast, the farther to the sea, the higher and wider the dunes are. However, the division by sand dunes and the system of roads and canals creates complex terrain. Particularly in the south of the province is lowland, divided by sand varieties into many local low-lying areas, this place is often flooded with salt water every year for 3-5 months.
River:
Tra Vinh has an extensive river system with a total length of 578 kilometers. Among these rivers, the Hau River and the Co Chien River are the important ones. The smaller rivers, canals, and streams in the Trà Vinh area predominantly flow into the sea through two main river mouths: the Co Chien River mouth, also known as Cung Hau, and the Định An River mouth.
Climate:
Tra Vinh has sunlight and stable temperature. However, due to its proximity to the sea, the province faces climate limitations such as strong winds, high evaporation and little rain. With a temperate tropical climate, an average temperature of 20 – 27 °C and an average humidity of 80 – 8000% per year, Tra Vinh is less affected by storms and floods. The rainy season lasts from May to November, and the dry season from December to April next year, with an average rainfall of 1,400 – 1,600mm. This creates favorable conditions for investment, business and tourism.
Each year, drought is a challenge for production in Tra Vinh, with a rain-free period of 10 to 18 days. Cau Ke, Cang Long and Tra Cu districts are less affected. Tieu Can district suffers from drought at the beginning of the crop in June and July, while Chau Thanh, Cau Ngang and Duyen Hai suffer from drought in the middle of the crop, especially in July and August.
In addition, Tra Vinh also faces the problem of mangroves in some dry seasons of the year, causing current difficulties for the province.
Natural resources
Tra Vinh province has 24,000 ha of forest and forest land, mainly along the coast. The total area is 229,200ha, including agricultural, forestry, specialized, rural and urban land. There are 3 main soil groups: sandy soil, alluvial soil and alkaline soil. The aquaculture area is 62,000 ha, with an average aquatic and seafood output of 157,000 tons/year. Main minerals include sand and clay bricks used in industry and construction, along with a mineral water mine meeting national standards in Duyen Hai town.
Socioeconomic:
Economy
In 2018, Tra Vinh had 1,049,800 people, GRDP reached 45,778 billion VND ($2,0061 billion), GRDP per capita was 44 million VND ($1,911) and GRDP growth rate was 9.56%. In 2012, the province sets a GDP growth target of 13.5% or more, in which sectors such as agriculture, forestry, fisheries, industry, construction and services all have different growth rates. Per capita income reached 19,325 million VND (920 USD), export turnover reached 200 million USD, an increase of 15.4% compared to 2011. The province also aims to reduce the poverty rate and create new jobs. Tra Vinh Sea is a large fishing ground of Vietnam with a seafood reserve of 1.2 million tons and a fishing capacity of 630,000 tons/year.
Residential:
In Tra Vinh, there are 3 main ethnic groups: Kinh (69%), Khmer (29%) and Chinese (2%). The population reaches 1,009,168 people, of which 17.2% live in urban areas and 82.8% in rural areas, with a population density of 414 persons/km² and a population growth rate of 0.06% in 2019. This province is home to Khmer people with a unique culture, including language, writing, food and temple system. The main language is Vietnamese.
As of April 1, 2019, the province has 12 religions with a total of 913,541 followers. Buddhism accounts for the largest number (769,990 people), followed by Catholicism (76,992 people), Cao Dai (45,226 people) and other religions such as Protestantism, Islam, Hoa Hao Buddhism, Buu Son Ky Huong, The Way of the Four Enthusiasm, the Master of the Way, the Way of the Way, and the Baha’i.
Traffic:
Tra Vinh has 3 main national highways, 53, 54 and 60, connecting this province with Ho Chi Minh City. Ho Chi Minh and the provinces of the Mekong Delta. Dai Ngai Bridge (unfinished) and Co Chien Bridge (completed) connect Soc Trang – Tra Vinh – Ben Tre province. Distance from the provincial capital of Tra Vinh to the city. Ho Chi Minh City is 200 km (under NH.53) and 120 km (under NH.60).
Waterway traffic of Tra Vinh is very convenient with a coastline of over 65 km, surrounded by Tien and Hau rivers and two estuaries of Co Chien and Dinh An. Waterway from Tra Vinh to Ben Tre, Tien Giang, City. From Ho Chi Minh City along the Tien River and from the East Sea through the Tra Vinh Canal to Can Tho Port is the main waterway transport route of the Mekong Delta region.