Song Doc Industrial Park
- Investor: Song Doc Industrial Park Infrastructure Investment Construction Joint Stock Company
- Price: 50 USD/m2
- Area: 145.45 ha
Ca Mau Province is a coastal province located in the southernmost part of Vietnam, situated in the Mekong Delta region. The entire area of Cà Mau is located on the Cà Mau Peninsula. In 2019, Cà Mau ranked 26th in terms of population among the administrative units in Vietnam, 41st in terms of Gross Regional Domestic Product (GRDP) on its territory, and 38th in terms of per capita GRDP. With a population of 1,229,600, the GRDP of Cà Mau reached 53,229 billion Vietnamese Dong (equivalent to 2.3118 billion USD), and the per capita GRDP stood at 47.1 million Vietnamese Dong (equivalent to 2,028 USD). The GRDP growth rate was 7.00%.

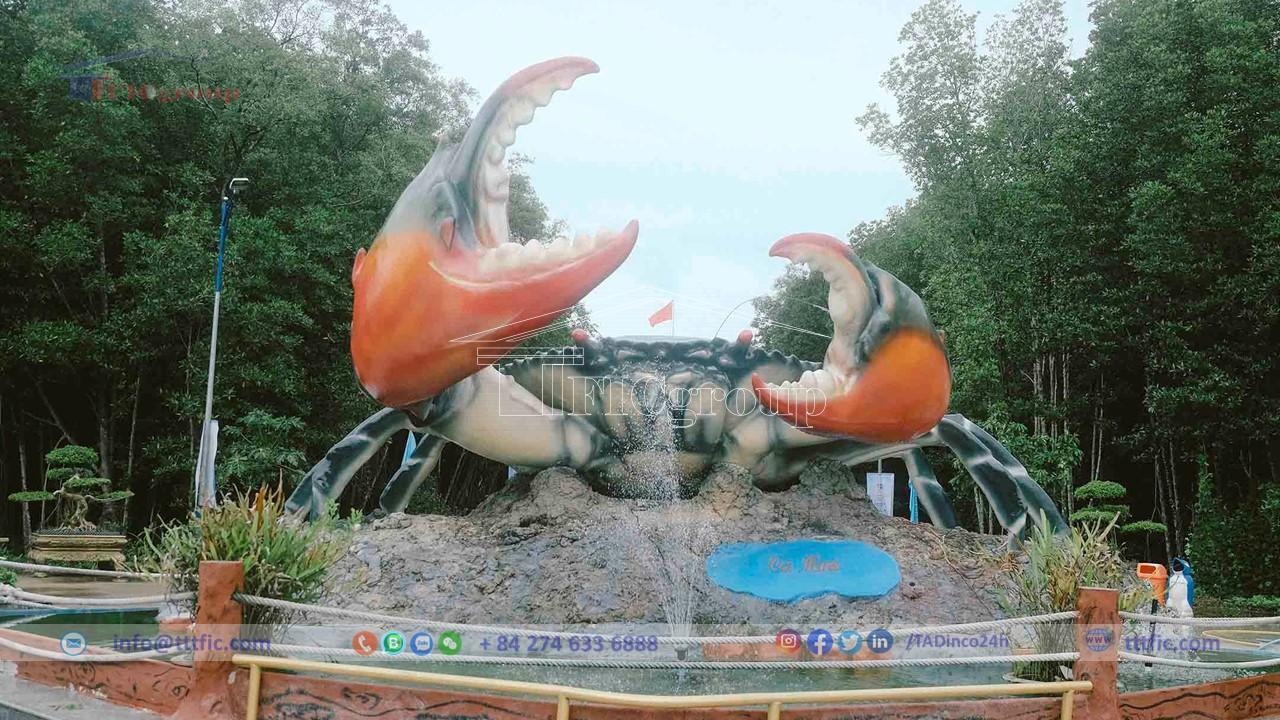
The Ca Mau Province is a relatively young land that has been developed for just over 300 years. It was initially explored by Mac Cuu, who led a group of Chinese immigrants to the Cà Mau region. After Mac Cuu offered the entire land to the Nguyen Dynasty, his son, Mac Thien Tu, followed the order of the Nguyen court and established the Long Xuyen administrative division. After several administrative changes, on January 1, 1997, Cà Mau province was reestablished according to the Resolution of the 10th session of the 9th National Assembly held on November 6, 1996, regarding the adjustment of administrative boundaries, dividing the Minh Hai province into Cà Mau and Bạc Liêu provinces.

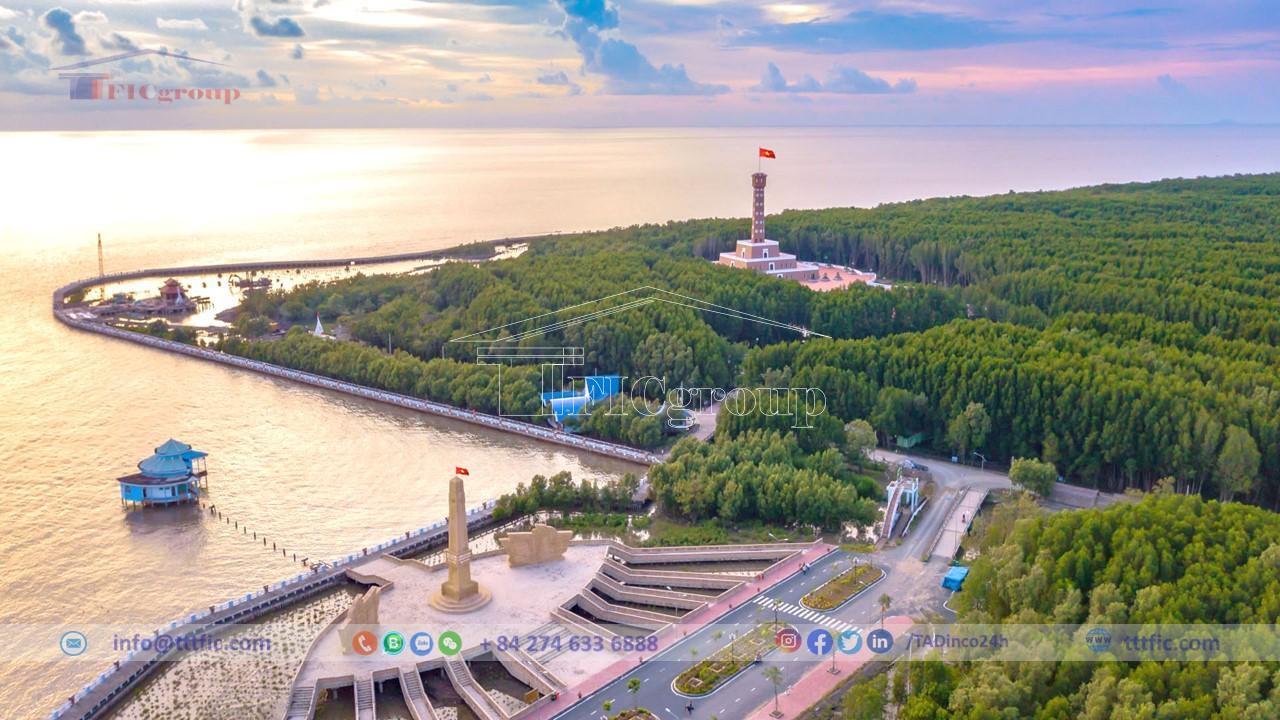
Despite initial poor economic and social conditions, Cà Mau has experienced significant growth and transformation. The agricultural sector’s dominance has decreased to 8%, while industry and services have flourished at 43% and 49% respectively.
In agriculture, rice cultivation covered a substantial portion of the province’s crop area, yielding 532,000 tons in 2011. Livestock farming faced challenges, with a shift towards shrimp farming due to feed shortages and salinity issues.
Cà Mau boasts concentrated forests and vast aquaculture areas, with aquaculture production increasing by 4.4 times since 1997. Shrimp farming dominates the sector, while seafood capture focuses on offshore fishing for sustainability.
Industrial and handicraft production has grown exponentially, with a value of 17,500 billion VND in 2011. Budget revenue and electricity production have also shown positive trends.
By 2019, Cà Mau’s GDP experienced a 7% increase, with a diverse economic landscape. Social investment and budget revenue exceeded expectations, driving development in agriculture, industry, and services. The province has demonstrated its potential for growth and economic prosperity.
As of April 1, 2019, Cà Mau had a total population of 1,194,476, with males accounting for 50.64% and females for 49.36%. The urban population constituted 22.69% of the total, while the rural population comprised 77.31%. The urbanization rate reached 28.4% by 2022.
The majority of the population in Cà Mau is of the Kinh ethnicity (97.19%), followed by the Khmer (2.19%) and the Hoa (0.53%). Other ethnic groups make up the remaining 0.1%.
Cà Mau has a population density of 229 people per square kilometer, lower than the regional average (423 people per square kilometer) and the national average (290 people per square kilometer). The city of Cà Mau has the highest population density at 908 people per square kilometer, while Ngọc Hiển district has the lowest at 94 people per square kilometer.
The gender ratio in Cà Mau is 102.6 males per 100 females, higher than the national and regional averages. The province has a “golden population structure” with 68.78% in the working-age group and 31.22% as dependents.
The crude birth rate in 2019 was 11.2 births per 1,000 people, and the sex ratio at birth was 102 boys per 100 girls, both lower than the national and regional averages. The average life expectancy in Cà Mau is 75.0 years, with males at 72.6 years and females at 77.5 years.
The living conditions of ethnic minority communities in Cà Mau have improved, with access to housing, clean water, employment opportunities, and education. Infrastructure development has focused on rural electrification, transportation, schools, healthcare facilities, and clean water supply. The poverty rate among ethnic minorities has decreased by 3-4% annually.
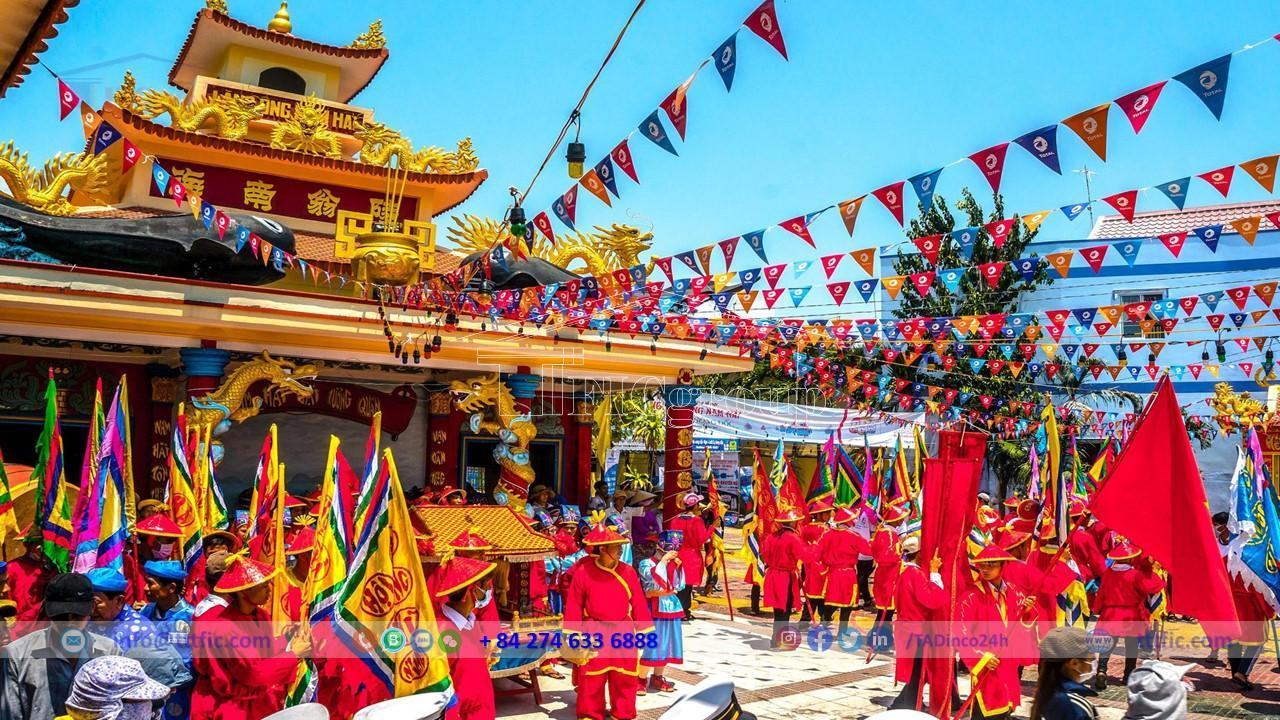

Cà Mau is home to various religious groups, including Buddhism, Catholicism, Protestantism, Cao Đài, and Hoa Hao. Various religious groups exist in the province, with Catholics being the largest (58.51%), followed by Buddhists (25.78%) and Cao Đài followers (8.76%). These communities actively engage in social welfare activities, supporting the poor, improving rural infrastructure, and providing healthcare services.
Overall, Cà Mau has made significant progress in improving the living standards and social conditions of its population. The province’s diverse ethnic groups contribute to its cultural diversity and unity.


