
Huu Thanh Industrial Park - Long An
- Investor: Industrial Development and Investment Corporation (IDICO)
- Price: $155 usd/m2
- Area: 524,14
Long An Province, located in the southwestern part of Vietnam, is one of the nation’s historical and rapidly developing provinces. With its strategic proximity to Ho Chi Minh City and international border crossings into Cambodia, the province holds immense potential for economic growth, industrial development, and foreign investments. Below is a detailed introduction to Long An Province, with an emphasis on its international border.
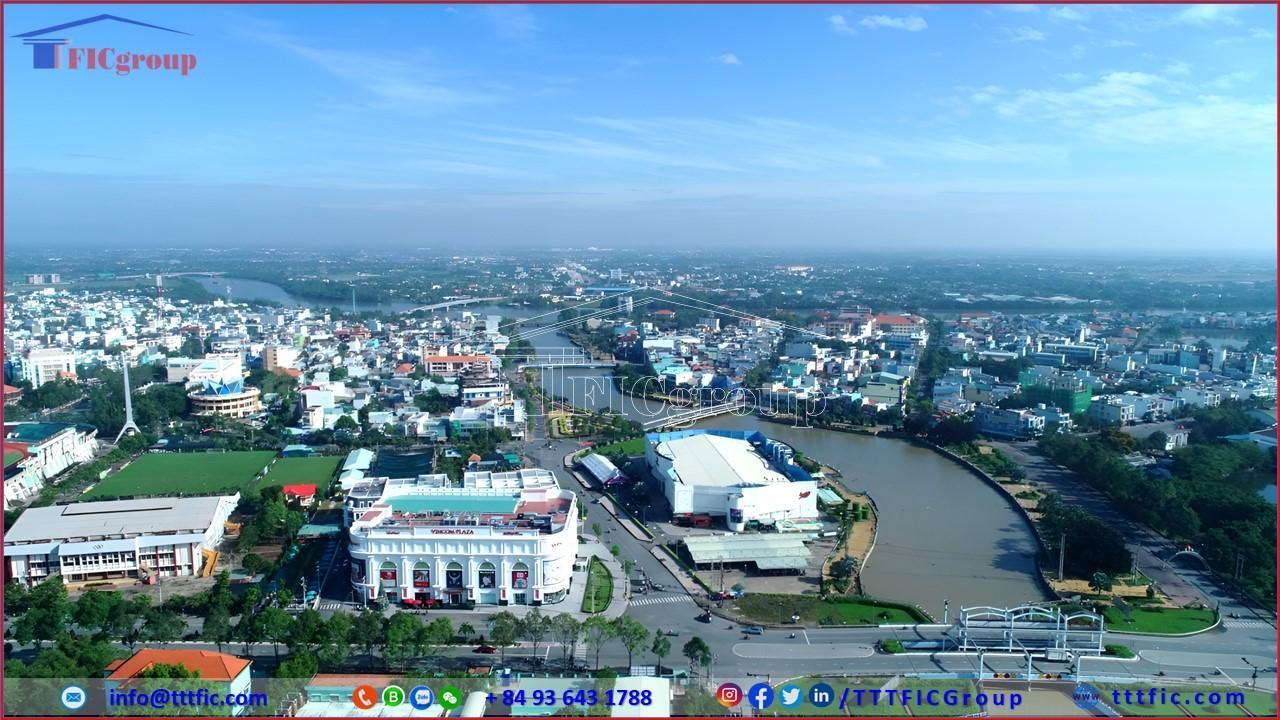

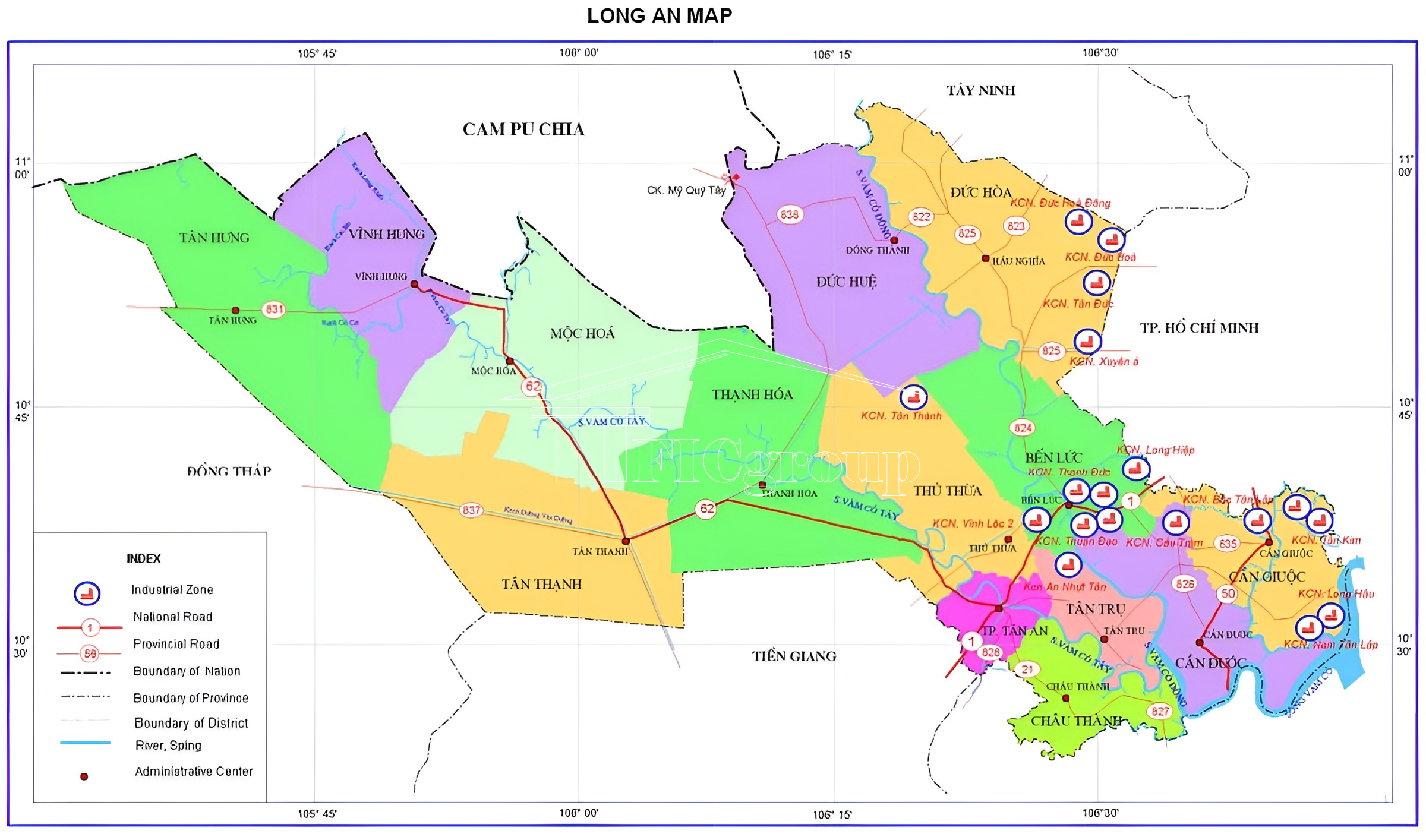
Long An province is located in the humid, tropical monsoon climate. As Long An province is bordered by the two regions of the Southeast and the Southwest. Long An province owns its special characteristics of the Mekong Delta and the distinctive ones of the Eastern region.
The average monthly temperature is 27.2 – 27.7 °C. Normally, the highest average temperature of 28.9 °C is in April, the lowest average temperature of 25.2 °C is in January.
Annual rainfall ranges from 966–1325 mm. The rainfall in rainy season is over 70–82% of the yearly rainfall. Rain distribution is uneven, decreased gradually from the area bordering Ho Chi Minh city to the West and Southwest. The minimum rainfall is in the Southeast districts near the sea. High mounds are eroded by the severity of heavy rain, which also creates inundation due to floods and high tides that disrupt people’s lives and work.
The average annual relative humidity is 80 – 82%. The average lighting time per day is from 6.8 – 7.5 hours/day and the average annual time is from 2,500 – 2,800 hours. Total annual temperature ranges from 9,700 – 10,100 °C. The temperature range between months of the year ranges from 2-4 °C.
The northeast wind with the frequency of 60 – 70% is in the dry season from November to April. The southwest wind with the frequency of 70% is in the rainy season from May to October.
Long An province is located in a typical region of sub-equatorial monsoon tropical climate with rich humid heat background, abundant sunshine, long radiation time, low and moderate round day temperature range between months of the year.
The outstanding differences in weather and climate as above directly impact on social life and agricultural production.
There are 15 district-level administrative units, including 1 city, 1 town and 13 districts with 188 commune-level administrative units, including 12 wards, 15 towns and 161 communes in Long An province.
Long An is home to approximately 1.5 million people, with Vietnamese being the predominant language. However, due to its diverse ethnic composition and economic development, various other languages and ethnic dialects are also spoken.
Famous for such many agricultural products as Tai Nguyen rice, Nang Thom Cho Dao rice, De Go Den wine, Long Tri watermelon, Ben Luc pineapple, Duc Hoa peanut, Thu Thua sugarcane, Chau Thanh dragon fruit,… Especially, high-quality rice is a key agricultural product for export.
Industry accounts for about 50% of the provincial economy’s value, with such products as textiles, processed foods, construction, etc. In the ranking of provincial competitiveness index (PCI) of Vietnam in 2018, Long An province ranked at the 2nd out of 13 western provinces and the 3rd in the whole country.
It is is estimated that the 2019 industrial production is VND 315,200 billion. It is is estimated that GRDP is VND 123,000 billion. Budget revenue is VND 18,000 billion.
Long An maintains a diverse economy, rich in natural resources and a robust agricultural sector. Agriculture and agro-processing industries play a pivotal role in the province’s economy, with notable crops including rice, maize, and famous catfish.
Yet, the province’s economic strengths extend beyond agriculture. Long An has attracted significant foreign investments, particularly in the industrial and service sectors. Industrial parks within Long An, such as Long Hau Industrial Park, Thanh Phat Industrial Park, and Duc Hoa Industrial Park, Xuyen A Industrial Park, Vinh Loc 2 Industrial Park, Hai Son Industrial Park have drawn numerous businesses, creating substantial employment opportunities for its residents.

Duc Hoa 3 Industrial Parks are prominent industrial zones in Long An Province, facilitating economic growth and international trade. Here is a list of some of these industrial parks and their names:
These industrial parks contribute significantly to the economic development of the Long An region and offer various opportunities for businesses and investors seeking to operate in Vietnam’s growing industrial sector.
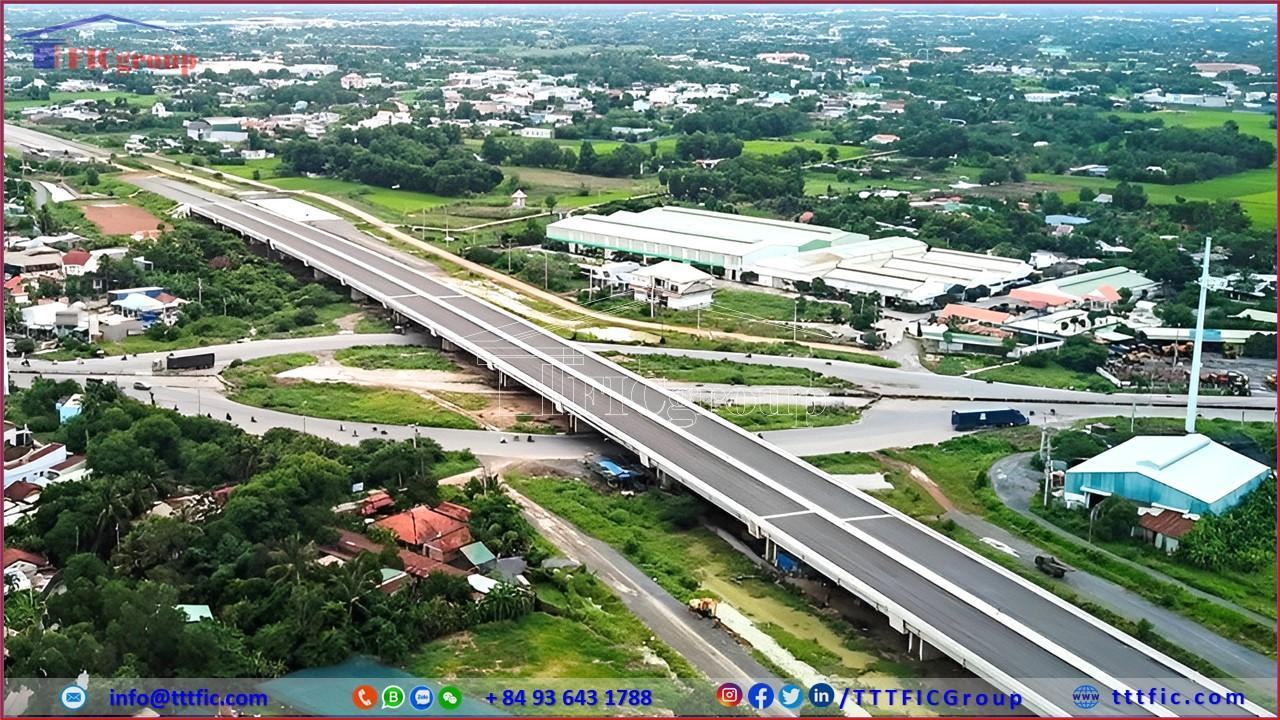
Long An province is the gateway linking the Southeast to the Mekong Delta, sharing a border with Ho Chi Minh city. The transport system linking Long An province to the region is quite complete, including road and waterway.
National highways – expressways:
Existing: 1, 50, 62, Ho Chi Minh road, Ho Chi Minh city – Trung Luong expressway.
Expected: 50B (HCMC – Long An – Tien Giang Motive road), N1, Ben Luc – Long Thanh Expressway, Ring Road 3, Ring Road 4.
Provincial roads are numbered 816 – 840.
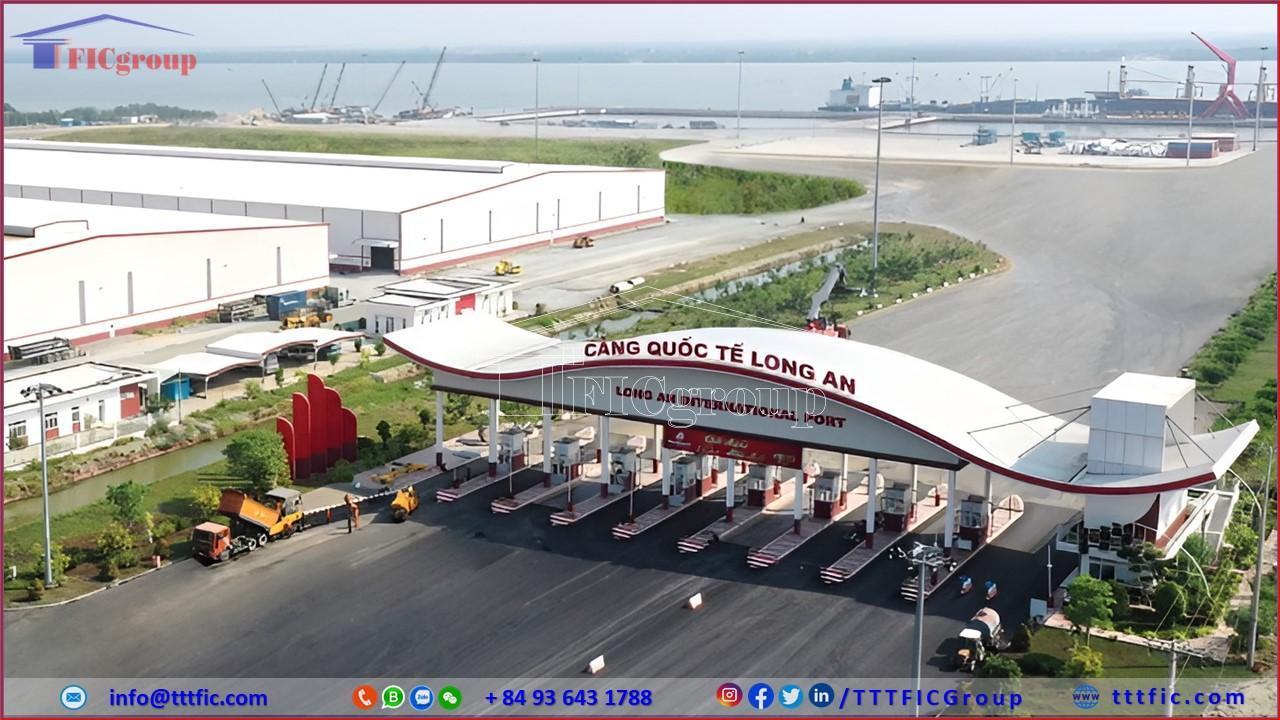
In addition to the road traffic system, Long An is a province with an interlaced waterway system with traffic routes such as Vam Co Dong river, Vam Co Tay river, Rach Cat river (Can Giuoc river). Important waterways such as Ho Chi Minh city – Kien Luong, Ho Chi Minh city – Ca Mau, Ho Chi Minh city – Tay Ninh all pass through Long An province along Nuoc Man canal, Rach Cat river, Vam Co Dong river. The types of water transport over 100 tons can follow canals such as Phuoc Xuyen, Duong Van Duong, Tra Cu, Kinh Xang, Ben Luc river, Rach Cat river, Thu Thua canal… going from the West to Ho Chi Minh city.

Long An shares a national border with Cambodia that spans 137.7 kilometers. It features two international border crossings, Binh Hiep (Moc Hoa) and Tho Mo (Duc Hue). These border crossings are crucial for trade and diplomatic relations between Vietnam and Cambodia, further enhancing Long An’s strategic importance on the international stage.
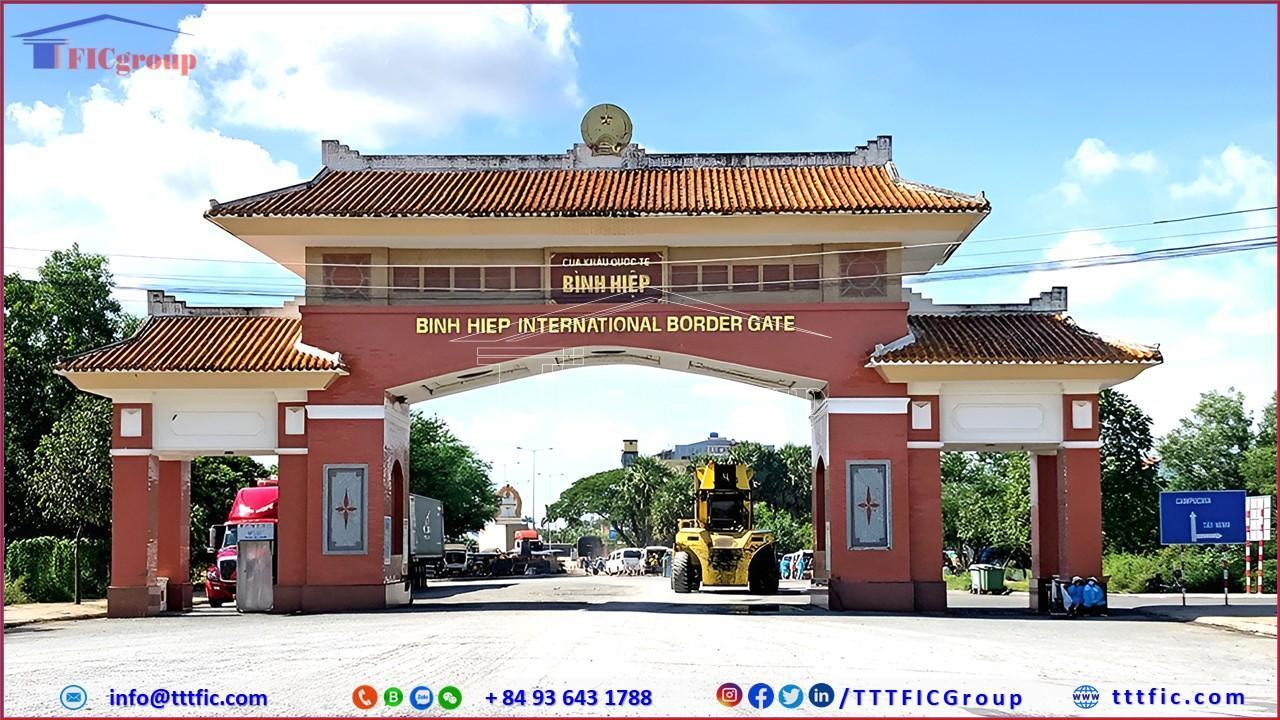

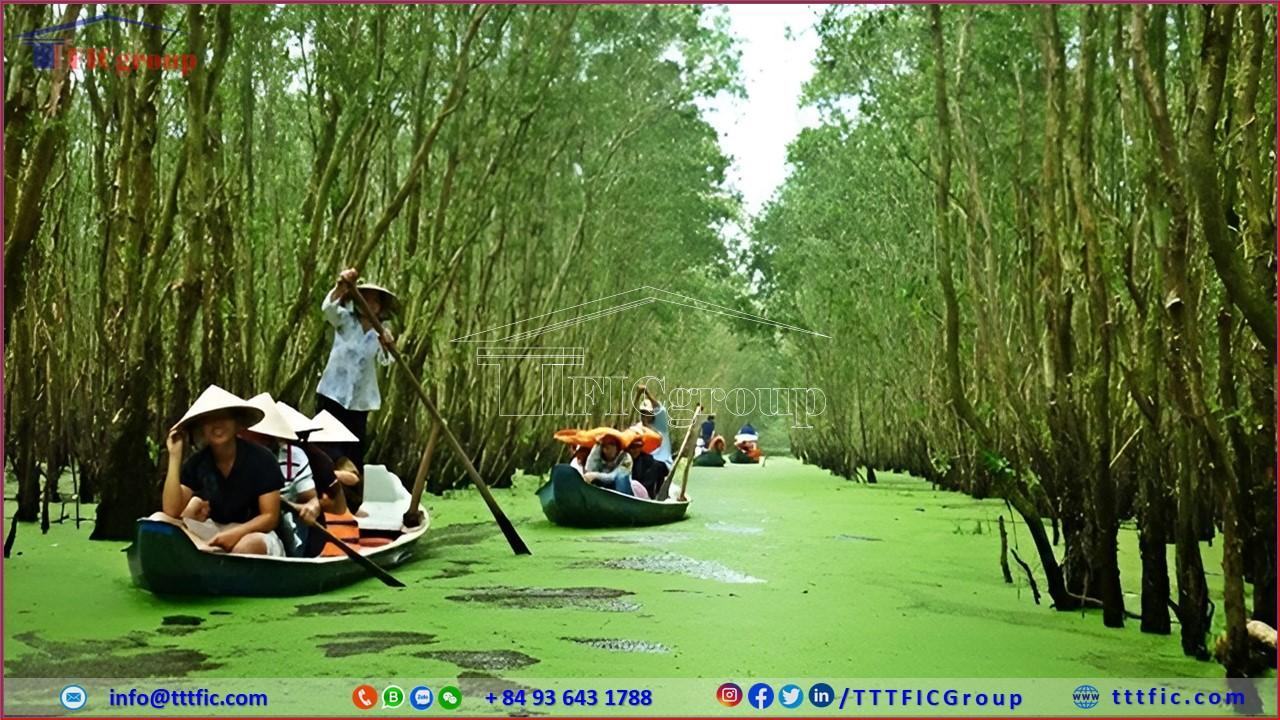
Long An boasts a unique cultural heritage with a long history. Traditional festivals such as the Co Ong Temple Festival and the Chau Van Festival showcase the diversity and richness of the local culture. The province also offers numerous tourist destinations, including Dong Thap Muoi Eco-Tourism Area, Gò Đậu Waterfall, and Can Giuoc Eco-Tourism Area, which attract many visitors.

Long An has been actively investing in education and research. The province is home to several notable universities, high schools, and colleges. Prominent institutions like Tay Do University and the High School for Natural Sciences and Engineering provide opportunities for education and career development.
Long An is committed to sustainable development, emphasizing environmental conservation and responsible resource management. The province is investing in renewable energy projects and infrastructure improvements to mitigate the impact of climate change.
Long An is a province with tremendous development potential, featuring a diverse economy, unique cultural heritage, and a commitment to sustainable growth. The presence of international border crossings adds to its significance, making Long An an attractive destination for both residents and entrepreneurs, and a vital player on the international stage.

We offer Information and Consultation Services for Industrial Real Estate, including leasing, buying, foreign direct investment (FDI), mergers and acquisitions (M&A), and legal consultancy for foreign investors.
Call us today for the best opportunities to expand your business into Vietnam! We specialize in M&A consultancy for industrial real estate in industrial zones throughout Vietnam.
————————————
Team Marketing
Tel: + 84 274 633 6888
Email: info@tttfic.com
Phone: + 84 916 974488
IG/Twitter/LinkedIn/page: /TTTFICGroup
Table of contents








